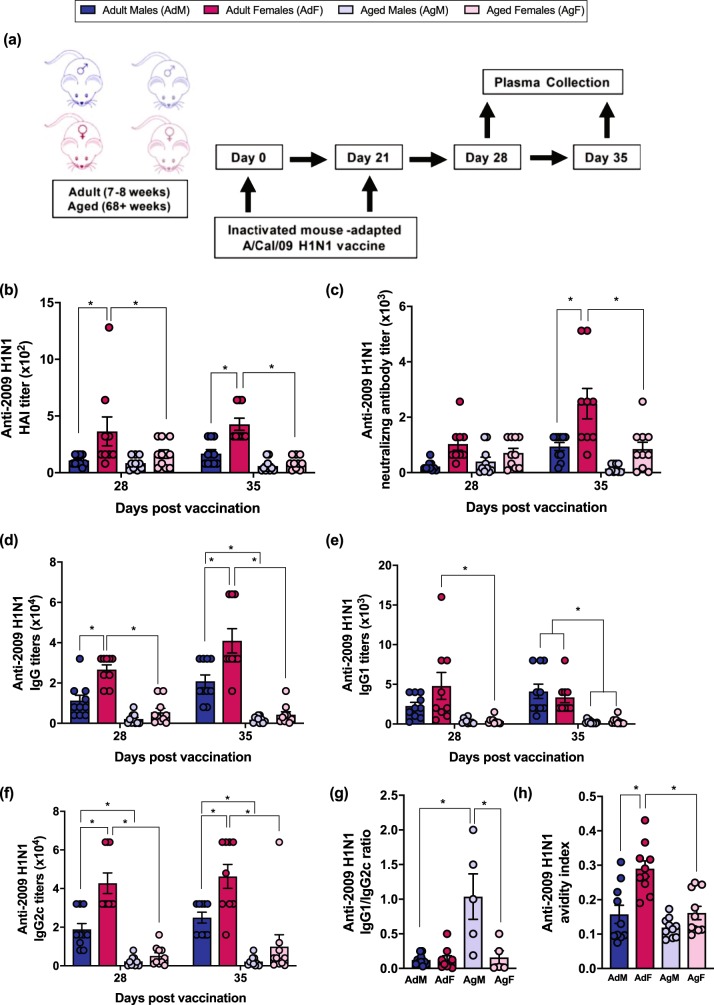
Fig. 2.
Adult female mice have greater antibody responses to an inactivated 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine than their male counterparts, which is mitigated in aged mice. Adult (8–10 weeks) and aged (68–70 weeks) male (dark or light blue, respectively) and female (dark or light pink, respectively) mice were vaccinated with an inactivated ma2009 H1N1 vaccine and plasma was collected on days 28 and 35 (i.e., 7 and 14 days post boost) (a). Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers (b), neutralizing antibody titers (c), anti-2009 H1N1 IgG (d), anti-2009 H1N1 IgG1 (e), anti-2009 H1N1 IgG2c (f), the ratio of IgG1/IgG2 (g), and antibody avidity (h) responses were measured. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean from two independent replications (n = 9–10/group) and significant differences between groups are denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.05) based on two-way ANOVAs (b–f) or one-way ANOVAs (g, h)