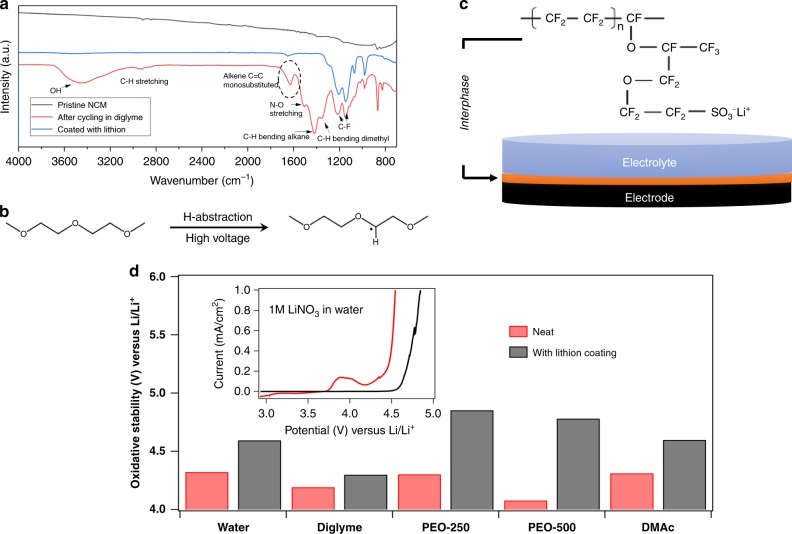
Fig. 2.
Designing stable cathode electrolyte interfaces (CEI) based on immobilized anions. a Intensity profile obtained from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) for pristine (uncycled) NCM and NCM cathode extracted from a Li||NCM cell cycled twice at C/10, with and without the Lithion coating. b Schematic showing the proposed proton extraction mechanism from the diglyme molecule due to oxidation at high voltages. c Schematic showing the structure of lithiated NafionTM (Lithion) utilized to form the artificial CEI. d Bar chart comparing the oxidative stability of different electrolytes with (black) and without (red) Lithion coating. The measurements were performed in 3-electrode cell with Ag/AgCl as reference and stainless steel as counter and working electrodes. The scan rate was 10 mV/s. The electrolytes investigated are 1 M LiNO3 in water, r = 0.1 LiNO3 in diglyme, r = 0.05 LiNO3 in PEO-250, r = 0.05 LiNO3 in PEO-500, and 1 M LiNO3 in dimethylacetamide. The inset shows results from linear scan voltammetry for the 1 M LiNO3(aq) electrolyte. All the voltages are shifted with respect to Li/Li+