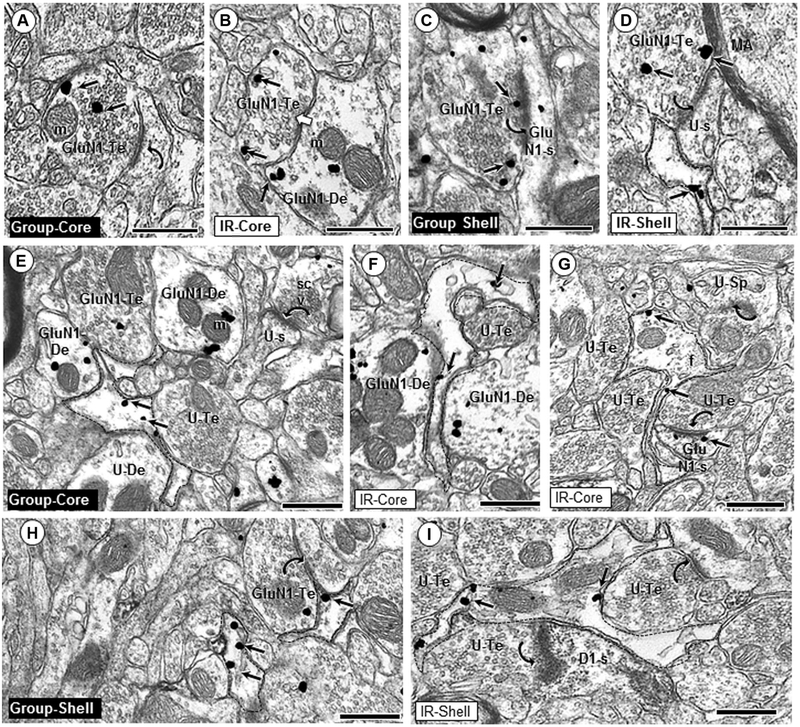
Fig. 4.
Glial and axonal GluN1 expression. GluN1 immunogold particles are present in axonal (a–d) and glial (e–i) profiles in the Acb core and shell of group- and isolation (IR)-reared adult rats. GluN1 immunogold particles (small arrows) are frequently in contact with non-synaptic plasma membranes in the interior of axon terminals (GluN1-Te; a, d, h), or localize near the synaptic active zone (c). GluN1-containing axon terminals often form asymmetric synapses (curved arrows; a, c, d) with dendritic spines in the Acb core and shell of both group and IR animals. GluN1 immunogold is also seen in axon terminals forming symmetric synapses (white block arrow, b). In both regions, GluN1 immunogold labeling is seen in filamentous glial processes (dashed outline; e–i) apposing unlabeled (U-Te; e, f, g) and GluN1-labeled (h, i) axon terminals, as well as unlabeled dendrites (U-De; e) and GluN1-labeled dendrites (GluN1-De; f). Asymmetric axospinous synapses (curved arrows) are typically seen in the neuropil near GluN1-labeled glial profiles (g, h, i). m mitochondria, U-s unlabeled spine, scv small clear vesicles, f intermediate filament; scale bar = 500 nm