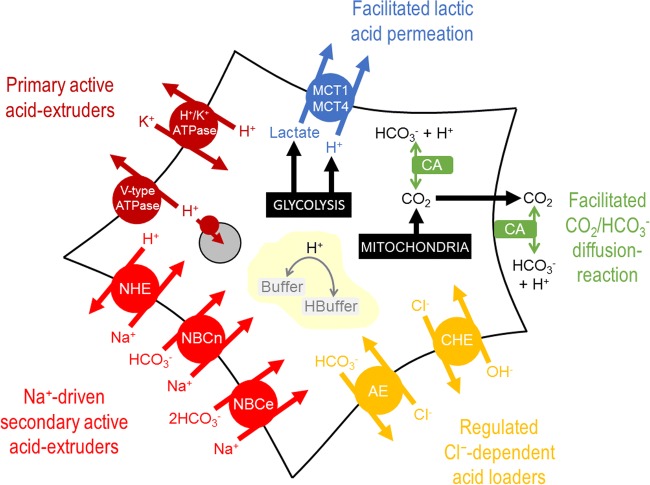
Fig. 1.
Schematic of a cancer cell, showing the major molecules involved in pH regulation. The complexity of the system is factually correct, but unpalatable for estimating the distribution of H+ ions fluxes through the various processes, deriving a value for the steady-state pHi, or predicting how the system would respond to changes in one or more of these processes. MCT: H+-monocarboxylate transport; CA: carbonic anhydrase; CHE: Cl−/OH− exchange; AE: anion exchange; NBCe: electrogenic Na+-HCO3− cotransport; NBCn: electroneutral Na+-HCO3− cotransport; NHE: Na+/H+ exchange; organelle: acidic lysosome/endosome with V-type ATPase