Figure 2 –
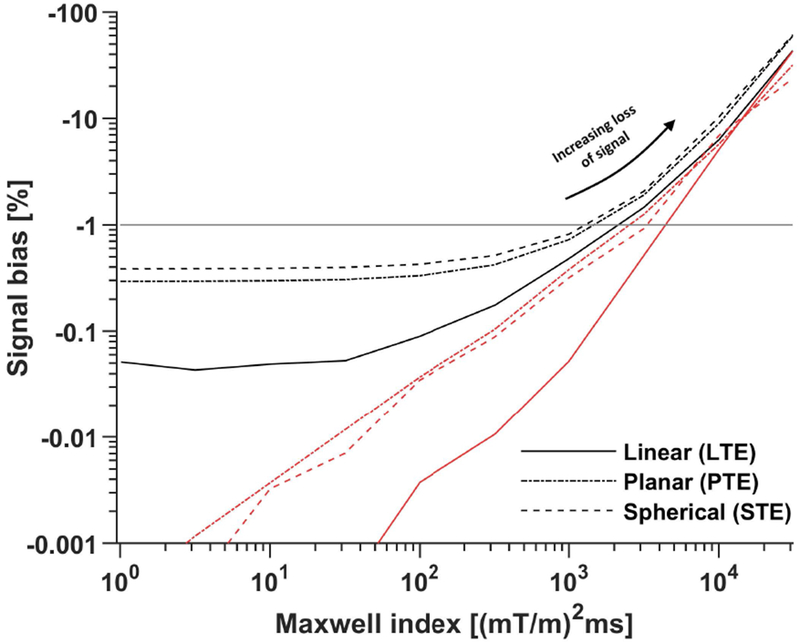
The signal bias (Eq. 13) depends on the Maxwell index constraint as well as the target b-tensor shape. The plot shows the simulated bias in the worst-case scenario when using interpolated (black) and original (red) waveforms optimized at a temporal resolution of N = 100 samples. It is clear that the interpolation worsens the Maxwell-compensation but does not elevate the signal bias beyond the tolerated level of −1 % (horizontal gray line). Furthermore, the signal bias becomes virtually independent of the Maxwell index when m is below approximately 100 (mT/m)2ms. This indicates diminishing returns for overly conservative optimization of m when the waveform must be interpolated in a later step. The median optimization time over 20 repeated optimizations for each m was between 2 and 30 s using an Intel Core i7-8750H.
