Figure 3. Perturbation series defined requirements for endogenous in situ brain tissue engineering.
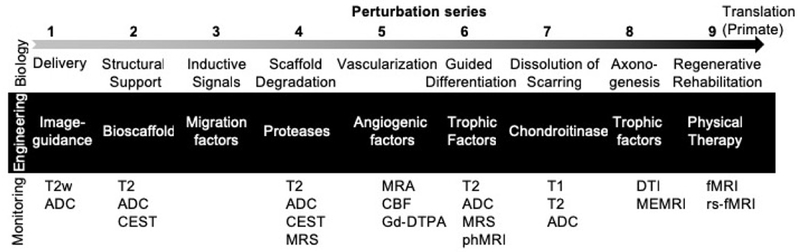
Based on endogenous tissue regeneration is peripheral soft tissue defects, 9 perturbation parts can be defined and arranged in a series to solve the same problem in the brain. For each biological challenge, an engineering solution can be envisaged. To ensure that these concerted parts unfold in vivo, ideally non-invasive monitoring is used to visualize and check that an appropriate biology continues to develop. Magnetic resonance imaging techniques, such as T2-weighted (T2w) images, T2 maps, Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), as well as functional brain imaging techniques, such as manganese-enhance MRI (MEMRI), functional MRI (fMRI), resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) and pharmacological MRI (phMRI) can be employed. To define the integrity of the blood brain barrier (BBB), gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) can be used to visualize leakage of molecules from the vascular compartment into the neuropil. A leaky BBB would occur during angiogenesis, when the barrier has not sufficiently matured and could hence indicate neovascularization.
