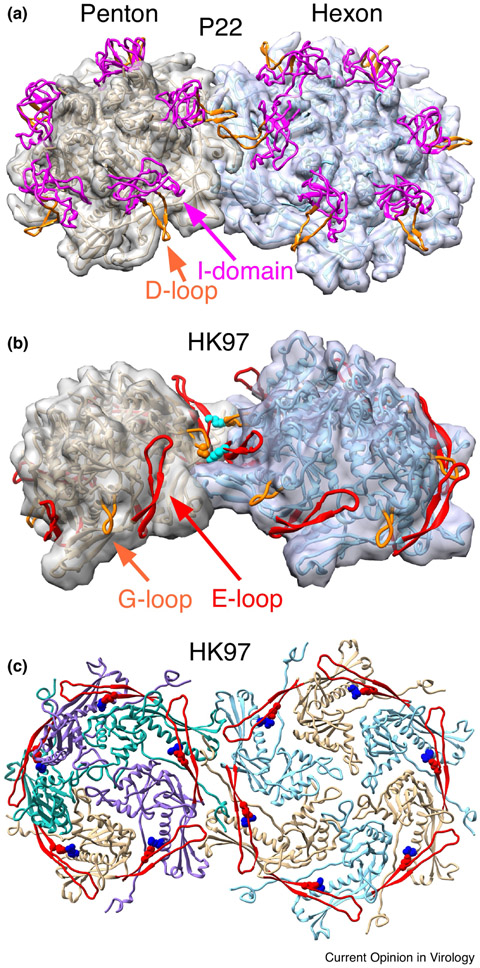
Figure 4. Capsid protein interactions that are important for assembly.
Inter and intra-capsomer interactions discussed in the text are illustrated in close-up views. A. The site of inter-capsomer interactions between phage P22 coat protein D-loops. This shows the interaction in the mature capsid [19], but similar interactions occur in procapsids during assembly [22,38,58]. B. Interactions between the E-loops (in red) and G-loops (in orange) of adjacent capsomers in HK97 procapsids (PDB ID 3e8k). These interactions (mediated by residues K178 (in cyan) on the E-loop and D231 (orange) on the G-loop) have been shown to be important for controlling the assembly of procapsids, but are not present in the mature capsid [13]. C. Interactions made by HK97 E-loops (shown as red ribbons) within capsomers. Residue E153 (in red) on the E-loop interacts with R210 (in blue) on the backbone helix of the adjacent subunit. These interactions are essential for assembly of the HK97 major capsid protein into procapsids [12]. The figure shows the mature capsid (PDB ID 1OHG), but the interactions are present at all stages of HK97 assembly.