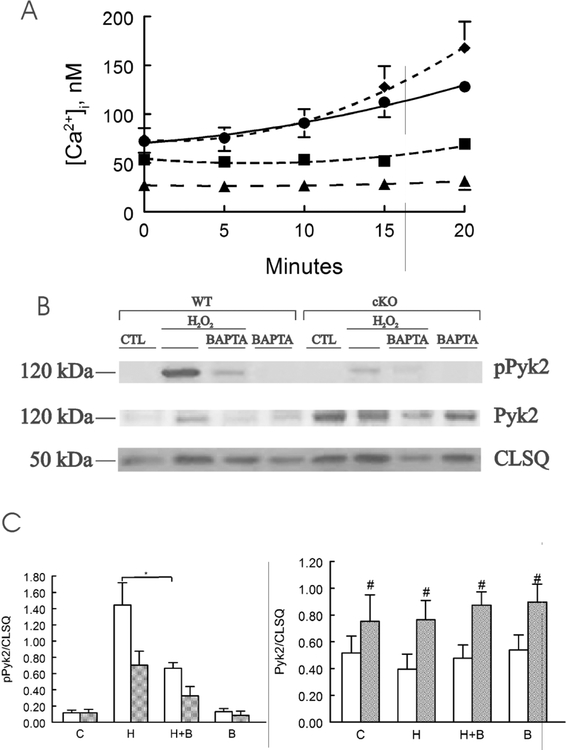
Figure 3. BAPTA buffers H2O2 induced [Ca2+]i increase and reduces Pyk2 phosphorylation in WT but not in cardiac-specific Trpm2 KO myocytes.
A. LV myocytes isolated from WT hearts were loaded with the Ca2+ indicator fura2 (0.67 μM fura-2 AM, 15 min, 37°C) before exposure to vehicle (■, n=4) or H2O2 (200 μM; ♦, n=4) and [Ca2+]i followed for 20 min. Some myocytes were pre-incubated with either 10 (•. n=4) or 50 μM (▲, n=4) of BAPTA-AM for 30 min before H2O2. B. LV myocytes isolated from WT and cKO hearts were treated with vehicle (CTL) or H2O2 (200 μM) for 15 min, with or without pre-incubation with BAPTA-AM (50 μM, 30 min), before harvest for immunoblotting. Representative blot of pPyk2, Pyk2 and calsequestrin (CLSQ; loading control) of 1 of 5 separate myocyte preparations. C. Summary of pPyk2/CLSQ and Pyk2/CLSQ for 4 WT (open bars) and 5 cKO (gray bars) myocyte preparations under control (C), H2O2 (H), H2O2 + BAPTA (H + B) and BAPTA (B) conditions. BAPTA significantly decreased pPyk2/CLSQ in WT (*, p=0.033) but not in cKO (p=0.1057) myocytes after H2O2 treatment. Total Pyk2/CLSQ in cKO was significantly higher (#, p=0.0020) than WT myocytes.