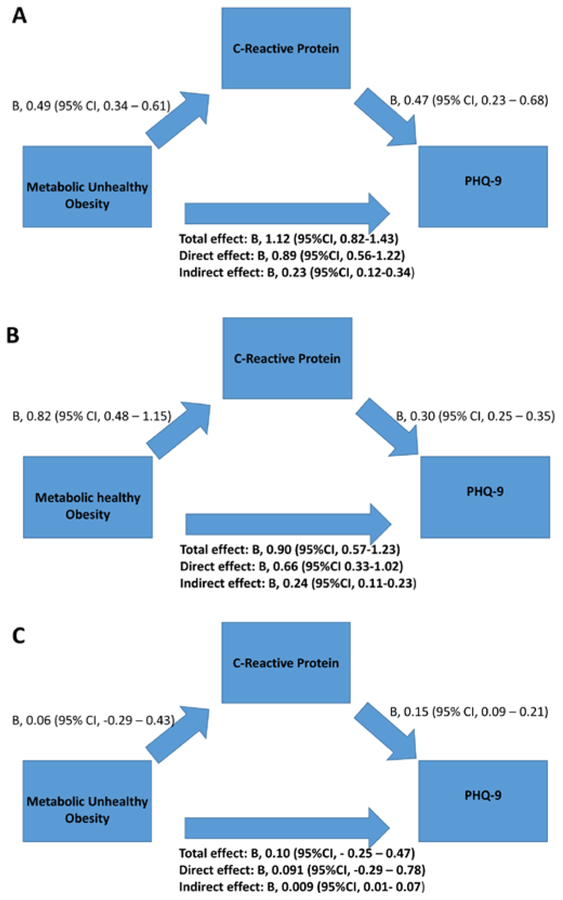
Figure 3. Mediation analysis for CRP levels as mediator of the relationship between metabolic unhealthy obesity and depressive symptoms.
A. Effect of Metabolic Unhealthy Obesity, compared with Metabolically healthy normal weight, on PHQ-9. B. Effect of Metabolic Healthy Obesity, compared with Metabolically healthy normal weight, on PHQ-9. C. Effect of Metabolic Unhealthy normal weight, compared with Metabolically healthy normal weight, on PHQ-9PHQ-9: Patient Health Questionnaire; Total effect: effect of metabolic subgroup on PHQ-9; Direct effect: effect of metabolic subgroup on PHQ-9 after controlling for CRP levels. Indirect effect: effect of metabolic subgroup on PHQ-9 through the CRP pathway, corresponding to the total effect minus the direct effect.
Model adjusted for demographic characteristics (age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, marital status, smoking history, physical activity, and household income)co-morbidities (coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, stroke, pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, and malignancy), and medication use (antidepressants and statins).