Figure 1. Schematic representation of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EC-EVs).
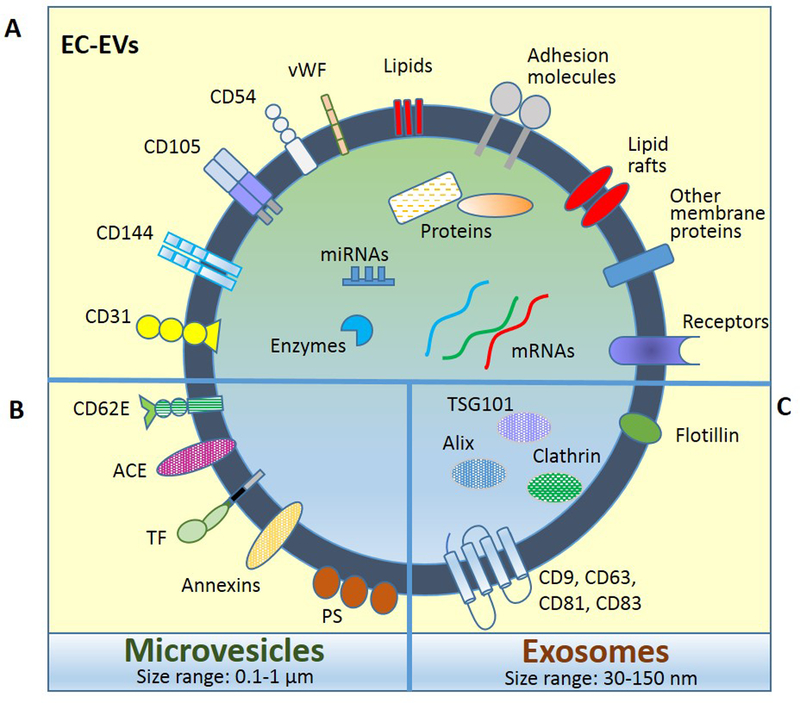
EV main categories, microvesicles and exosomes, carry common components (A) but also are enriched in specific molecules (B and C). EC markers that identify EVs of endothelial origin include CD62E, CD31, CD144, CD105, CD54, and vWF. Abbreviations: CD62E; E-selectin, CD31; PECAM-1, CD144; VE-cadherin, CD105; endoglin, CD54; ICAM-1, vWF; von Willebrand factor, ACE; angiotensin converting enzyme, TF; tissue factor, PS; phosphatidylserine, TSG101; tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein, CD9, CD63, CD81, CD82; tetraspanins.
