Fig. 1.
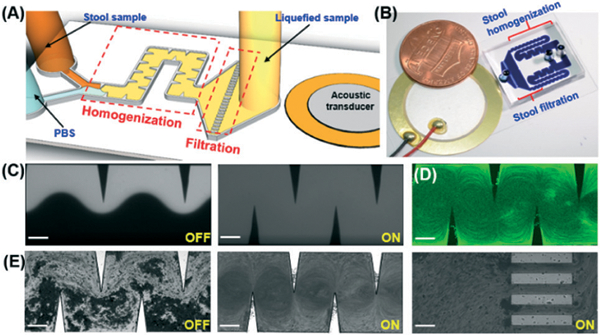
(A) Schematic and (B) photograph of the acoustofluidic-based stool liquefier device. (C) Characterization of high-performance mixing of DI water and fluorescent dye at 40 VPP and a total flow rate of 250 μL min−1 (125 μL min−1 in each parallel channel). With acoustics off (left), a laminar flow was observed and with acoustics on (right), complete mixing was obtained. (D) Characterization of strong acoustic micro-vortex streaming at 40 VPP and a total flow rate of 200 μL min−1 (100 μL min−1 in each parallel channel). (E) The stool liquefaction process was shown as follows: with the acoustics off (left), a laminar flow of stool sample and PBS flowed through the microchannel; with the acoustics on (center), strong acoustic micro-vortex streaming was created to mix stool samples; at the end of the channel (right), an array of 100 μm parallel microchannels designed as filters to remove large debris. Scale bar: 200 μm.
