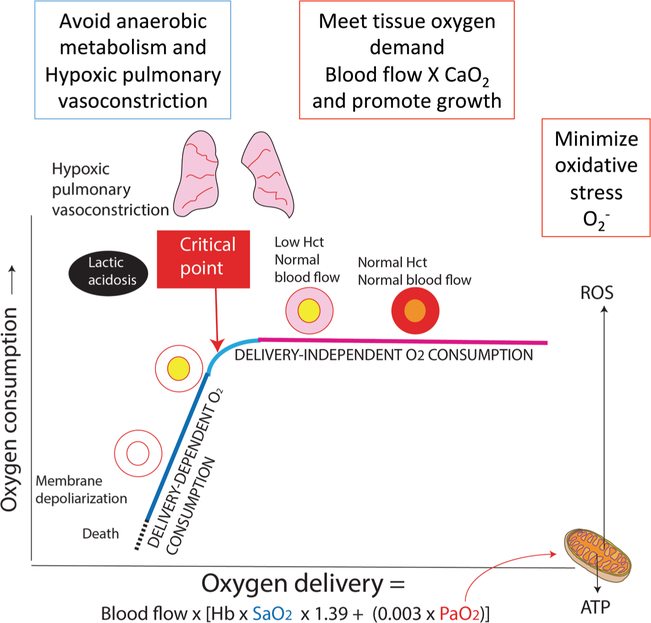
Fig. 4.
Relationship between oxygen delivery (DO2) and oxygen consumption (VO2). DO2 is a product of blood flow and arterial oxygen content (CaO2). The driving force for oxygen from alveoli to mitochondria is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2). Increased mitochondrial PO2 can lead to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). When DO2 decreases below a critical point, VO2 becomes dependent on delivery. Hypoxemia leads to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction, anaerobic metabolism, and lactic acidosis. Persistent hypoxemia can result in cell death.