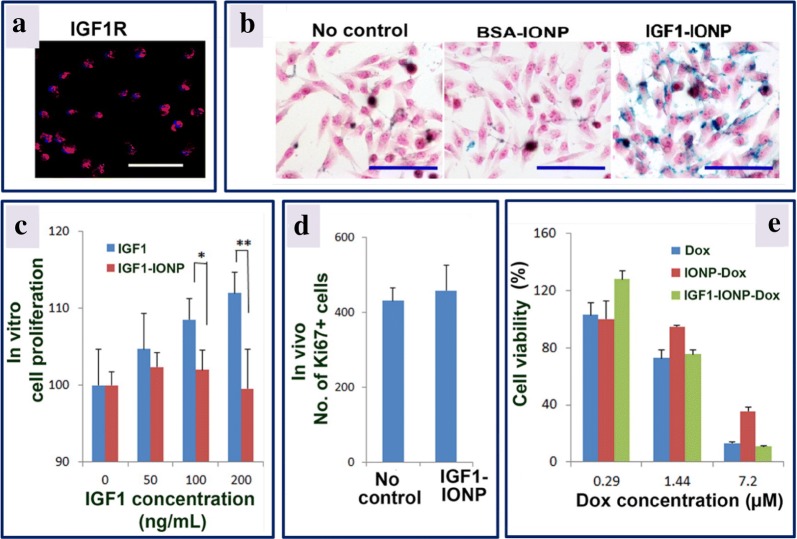
Fig. 3.
In vitro and in vivo effects of IGF1-IONPs (insulin-like growth factor 1-iron oxide nanoparticles) and IGF1-IONPs-doxorubicin on cell proliferation and viability. a The effect of IGF1R in MIAPaCa-2 cells was assessed by immunofluorescence labeling employing an anti-IGF1R antibody (shown in red color). b Prussian blue staining of cells incubated for 4 h with different treatments at 20 μg/mL of iron equivalent dose. The cells are also counterstained with nuclear fast red. c The in vitro influence of IGF1 and IGF1-IONPs on cell proliferation. The % of viable cells after 96 h incubation with IGF1 or IGF1-IONPs, and for 4 h at equivalent IGF1 concentrations was estimated by cell proliferation assay, wherein *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001. d The in vivo effect on tumor cell proliferation of IGF1-IONPs in human pancreatic PDX-tumor xenografts. By using immunofluorescence labeling of an anti-Ki67 antibody, the Ki67-positive cells in tumor sections after two tail vein injections of 20 mg/kg iron dose of IGF1-IONPs are measured. e In vitro cytotoxicity of unconjugated and conjugated doxorubicin in MIA PaCa-2 cells. The scale bars are 100 μm
(adapted with permission from [48])