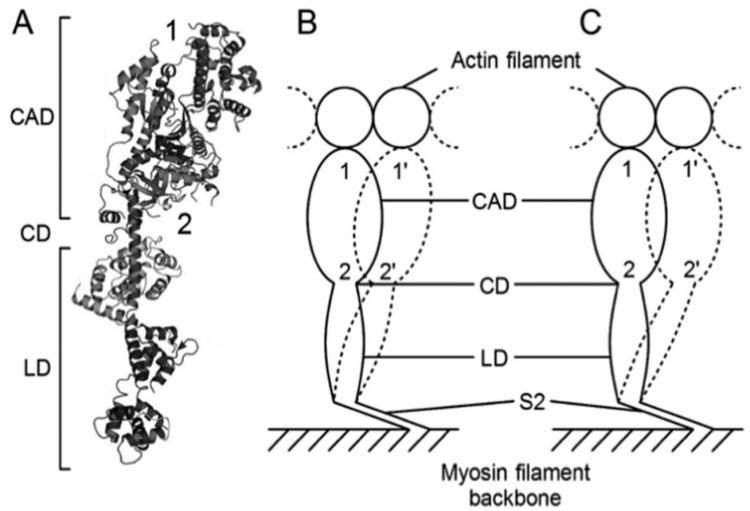
Figure 12.
Two different modes of ATP-induced myosin head power strokes. (A) Structure of the myosin head, which consists of a catalytic domain (CAD), a converter domain (CD), and a lever arm domain (LD). Approximate attachment regions of antibodies 1 and 2 are indicated by numbers 1 and 2, respectively. (B) The mode of myosin head power stroke at standard ionic strength. The amplitude of movement is larger at the distal CAD than at the proximal CAD so that the myosin head is oblique to actin and myosin filaments at the end of a power stroke. (C) The mode of a myosin head power stroke at low ionic strength. The amplitude of movement is the same at both the distal and the proximal CAD so that CAD is perpendicular to actin and myosin filaments at the end of power stroke. From Ref. [19].