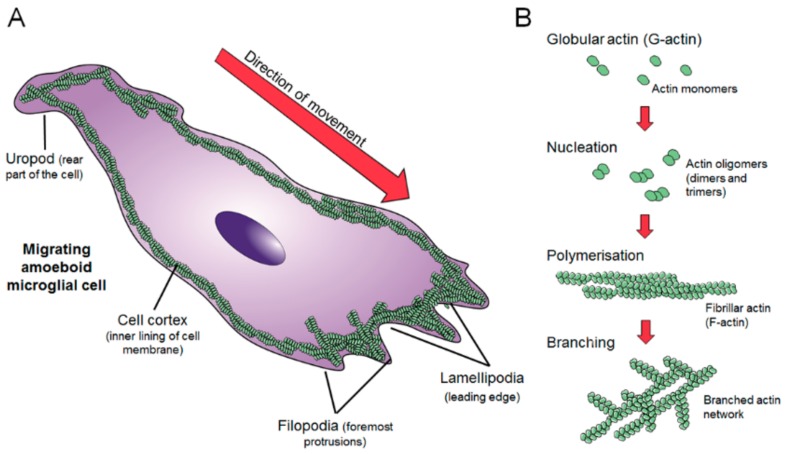
Figure 2.
(A) Depiction of the different actin structures present in microglia: The cell cortex (covering all the inner surface of the cell), filopodai and lamellipodia (at the leading edge), and the uropod (at the rear of the cell). (B) Mechanism of formation of the actin network includes globular actin nucleates in the form of oligomers which further polymerize into left-handed two-chained helical filaments. Filaments additionally recruit globular actin to form branches, which extend from the mother filament at a characteristic 70° angle enabling filaments to easily connect with each other forming an intricate and highly plastic network.