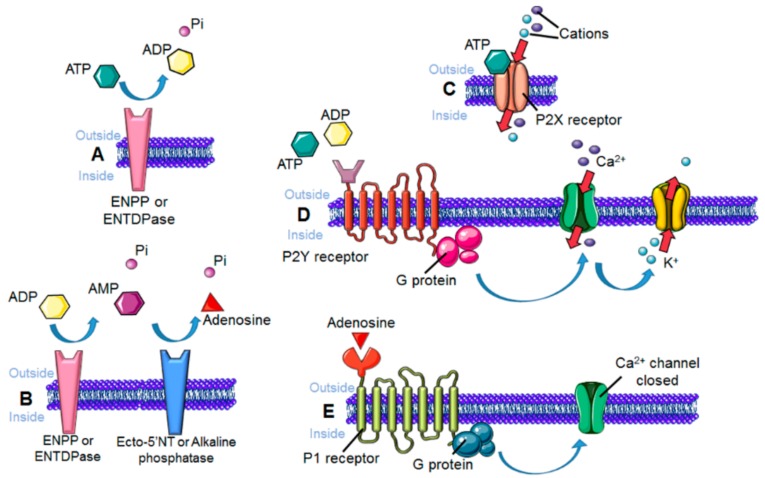
Figure 5.
Mechanism of activation of purinergic receptors. (A) Extracellular ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP by the action of ectonucleotide pyrophophatase/phosphodiesterases (ENPPs) or ectonucleoside triphosphate dyphosphohydrolases (ENTDPases). (B) ADP is subsequently hydrolyzed to AMP, also by ENPPs and ENTDPases. AMP is converted to adenosine by ecto-5′-nucleotidases (Ecto-5′-NTs) or alkaline phosphatases. (C) P2X cation-permeable ionotropic receptors are activated by nucleosides triphosphate. (D) G protein-coupled P2Y receptors regulate voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels. (E) Adenosine-mediated P1 receptor activation results in blockade of Ca2+ channels.