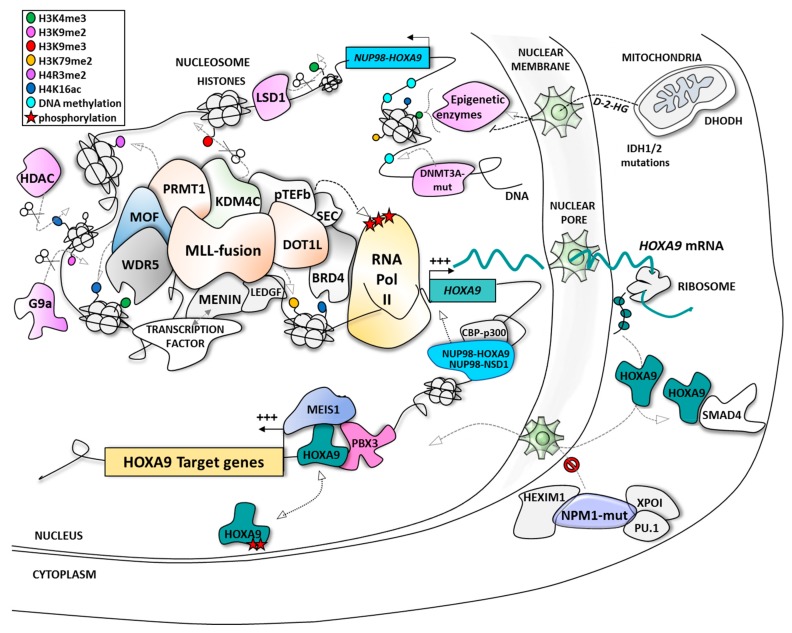
Figure 1.
The different modes of regulation of HOXA9 expression and function in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). BRD4, bromodomain-related protein 4; CBP, CREB-binding protein; CDK9, cyclin-dependent kinase 9; D-2-HG, D-2-hydroxyglutarate; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; DNMT3A, DNA methyl transferase 3A; DOT1L, disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like protein; HDAC, histone deacetylase; HEXIM1, hexamethylene bisacetamide (HMBA) inducible protein 1; HOXA9, homeobox A9; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; KDM4C/lysine-specific demethylase 4C; LEDGF, lens epithelium-derived growth factor; LSD1, lysine-specific demethylase 1; MEIS1, myeloid ecotropic viral integration site 1; MLL, mixed lineage leukemia; MOF, males absent on the first; NPM1, nucleophosmin 1; NSD1, nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1; NUP98, nucleoporin 98kDa; PBX3, pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 3; PRMT1, protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1; pTEFb, positive transcription elongation factor b; SMAD4, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4; WDR5, WD repeat protein 5; XPO-1, exportin-1.