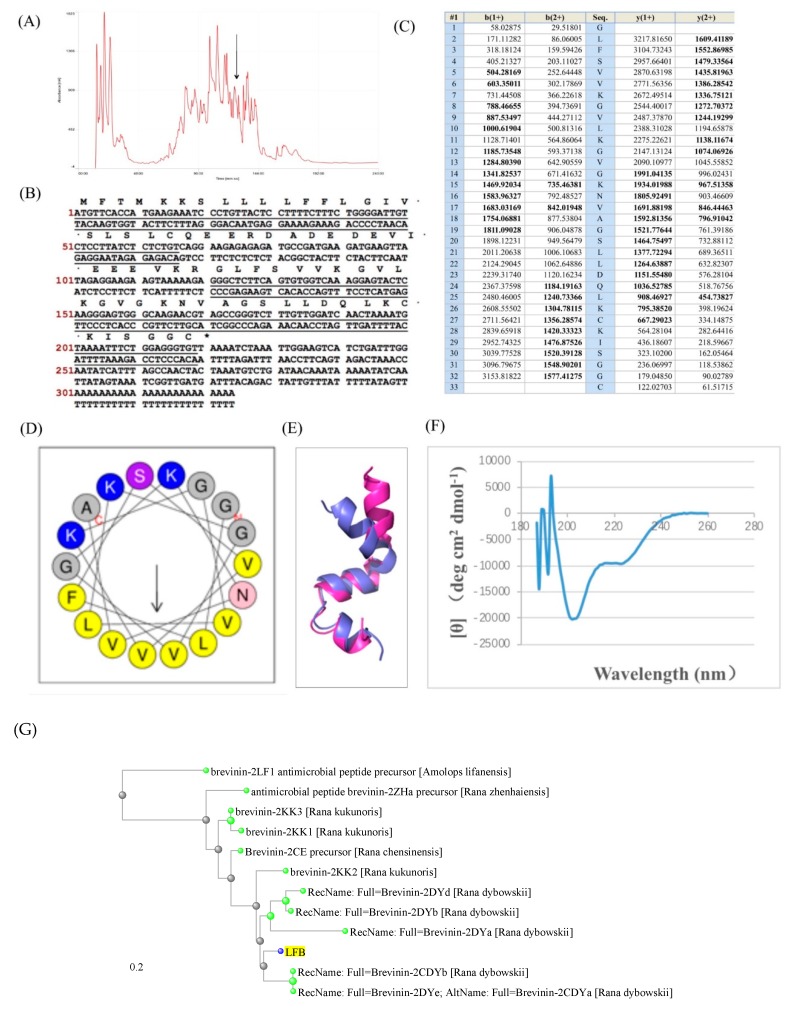
Figure 1.
(A) Region of reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatogram of Limnonectes fujianensis skin secretion indicating the elution position/retention time (arrow) of absorbance peak containing the peptide, Limnonectes fujianensis Brevinvin (LFB). (B) Nucleotide and translated open-reading frame amino acid sequence of the cloned cDNA encoding the biosynthetic precursor of LFB. The putative signal peptide is double-underlined and the mature LFB sequence is single-underlined. The stop codon was indicated with an asterisk. (C) Expected singly- and doubly-charged b-ion and y-ions arising from fragmentation of LFB as predicted using the MS-Product program available through Protein Prospector Online (http://prospector.ucsf.edu/prospector/mshome.htm). Observed fragment ions are indicated in bold typeface and are underlined. (D) Domain architecture of pre-LFB. Residues 1–22 constitute the putative signal peptide. Residues 23–40 constitute the acidic spacer peptide region typified by classical -KR- (-Lys-Arg-) pro-peptide convertase processing sites (italicized and in bold typeface). The single copy of mature LFB (residues 41–73) is underlined and in bold typeface. (E) Predicted protein structure of LFB. (F) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of LFB. The spectra have subtracted buffer. (G) The distance tree of LFB using NCBI BLAST.