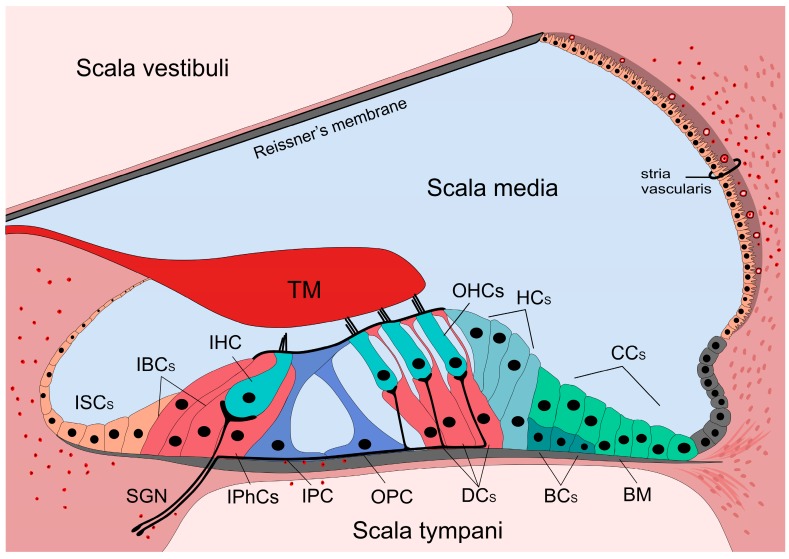
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the organ of Corti and the presence of immune cells. The cochlea is divided into three chambers (scalae) by two membranes. The organ of Corti is located in the scala media. The three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs) and the one row of inner hair cells (IHCs) are surrounded by different types of supporting cells. The cells are surrounded by the perilymph, but the stereocilia of the hair cells are bathed in the endolymph. The reticular lamina is formed by the apical parts of the cells establishing a barrier between the endo- and perilymphatic fluid compartments. The basilar membrane (BM) separates the scala media and tympani. Supporting cells (IBCs, IPhCs, IPC, OPC, DCs, HCs, CCs, BCs) span through the cellular layer of the organ while hair cells (IHC and OHCs) are not in direct contact with the BM, but their stereocilia reaches the tectorial membrane (TM). Resident macrophages and leukocytes are always present in the cochlea, primarily in the spiral limbus, in the scala tympani side of the BM as well as in the lateral wall. Red formations with black dots in the middle show position of these immune cells. ISCs: Inner sulcus cells; IBCs: Inner boarder cells; IPhCs: Inner phalangeal cells; IPC: Inner pillar cell; OPC: Outer pillar cell; DCs: Deiters’ cells; HCs: Hensen’s cells; CCs: Claudius’ cells; BCs: Boettcher’s cells. IHC and OHCs: Inner and outer hair cells; SGNs: Spiral ganglion neurons; TM: Tectorial membrane.