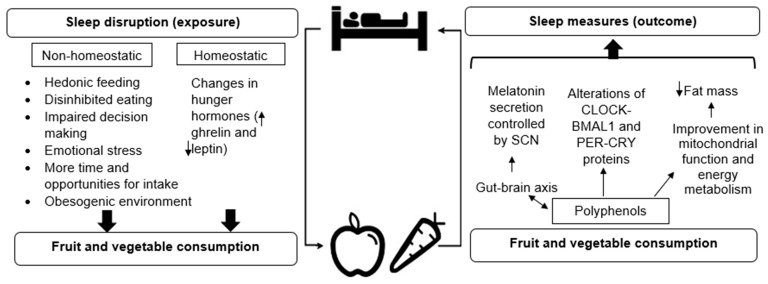
Figure 1.
Potential reciprocal mechanisms between sleep duration and fruit and vegetable consumption. Sleep disruption may influence dietary intake through non-homeostatic and homeostatic mechanisms. On the other hand, FV consumption may influence sleep through their polyphenol content through several potential pathways. With further research, other potential mechanisms may be identified. Legend: SCN (suprachiasmatic nuclei); CLOCK (circadian locomotor output cycles kaput); BMAL1 (brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 1); PER (period); CRY (cryptochrome).