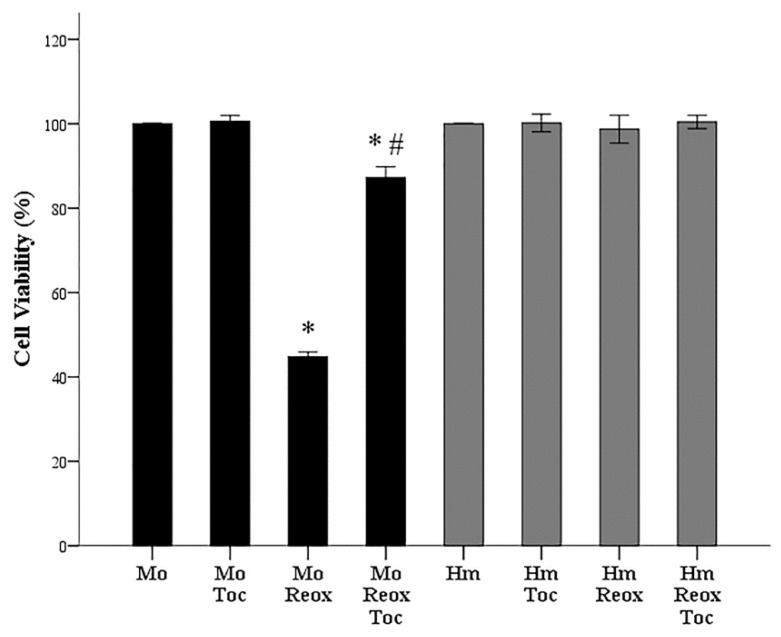
Figure 2.
Cell survival due to warm anoxia-reoxygenation and the effect of α-tocopherol. The XTT assay revealed that cell survival in mouse RPTECs was decreased in contrast to hamster RPTECs that well tolerated 24 h of anoxia followed by 2 h of reoxygenation. The presence of α-tocopherol (Toc) did not affect the cell viability of hamster RPTECs. However, it significantly enhanced cell viability of mouse RPTECs subjected to anoxia-reoxygenation. These experiments were repeated nine times in triplicate. Error bars correspond to SEM, the asterisk (*) to p < 0.001 when compared to the respective control cells, and the hashtag (#) to p < 0.001 between cells subjected to anoxia-reoxygenation without or with α-tocopherol. Mo stands for mouse, Hm for hamster, ctrl for control, Reox for reoxygenation, and Toc for α-tocopherol.