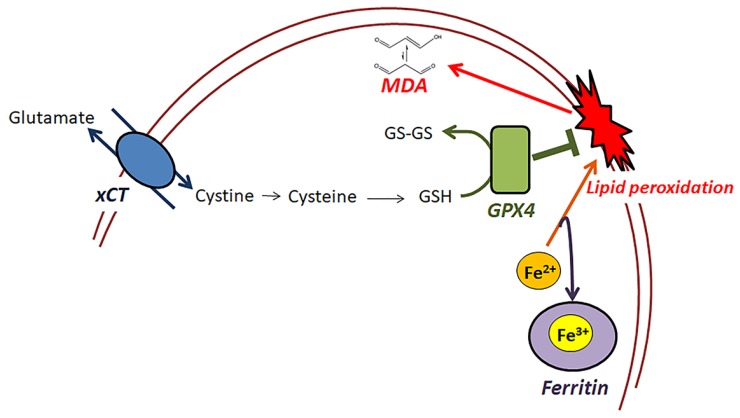
Figure 5.
Components of the ferroptotic pathway evaluated in the present study. In this study, the effect of warm anoxia-reoxygenation on the main initially discovered elements of the ferroptotic pathway was evaluated in RPTECs derived from mouse or the native hibernator Syrian hamster. The cystine-glutamine antiporter (xCT) facilitates the transport of cystine into the cells, which is required for the synthesis of glutathione (GSH). Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is the only GPX isoenzyme capable of reducing cell membrane polyunsaturated phospholipid hydroperoxides, and in this reaction, it oxidizes GSH. Labile bivalent iron (Fe2+) is necessary for cell membrane lipid peroxidation, while ferritin stores the labile bivalent iron in its nontoxic trivalent form (Fe3+) preventing lipid peroxidation. Our study showed that the lack of lipid peroxidation, assessed by the cellular malondialdehyde (MDA), in hamster RPTECs subjected to warm anoxia-reoxygenation might result from the increased xCT and ferritin expression.