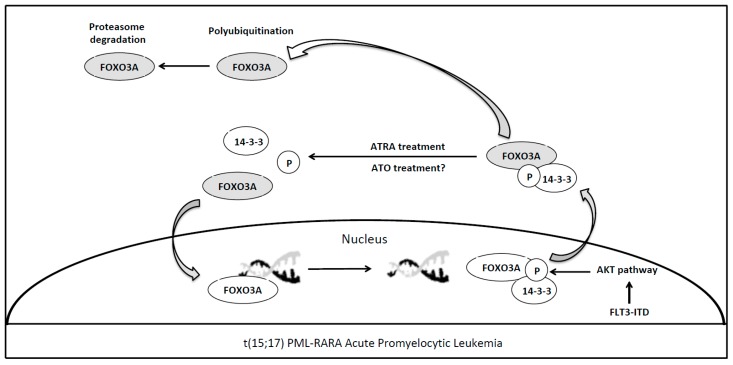
Figure 2.
ATRA mediated reactivation of FOXO3A in t(15;17) PML-RARA acute promyelocytic leukemia. Nuclear FOXO3A (active form), once phosphorylated, interacting with 14-3-3 protein is exported to the cytoplasm losing its function [52]. The phosphorylation of FOXO3A, and its consequent loss of function, may be regulated by AKT pathway aberrantly activated in case of AML driver mutations such as FLT3-ITD [53]. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) treatment is able to reduce FOXO3A phosphorylation and to induce the relocation of the transcription factor into the nucleus, where the protein leads to blast apoptosis [40]. Arsenic trioxide (ATO) treatment in this cellular context needs to be better assessed. Light grey shows the FOXO3A inactive form.