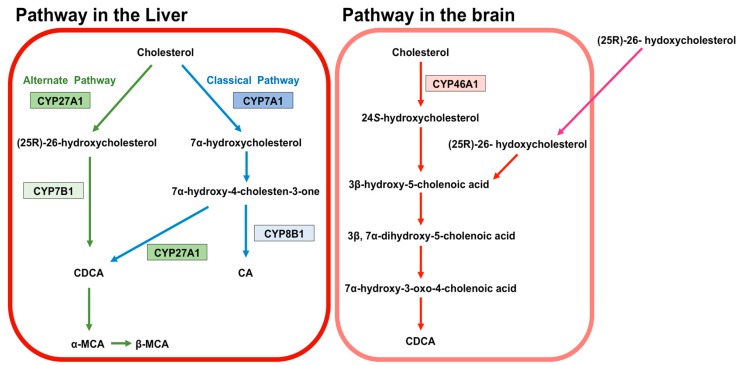
Figure 1.
Synthesis of bile acids (BA). The classical pathway is initiated by cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1). CYP7A1 converts cholesterol to 7α-hydroxycholesterol. 7α-hydroxycholesterol is then converted to 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one. Cytochrome P450 8B1 (CYP8B1) leads the production of CA from 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one. 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one is also converted to CDCA by cytochrome P450 27A1 (CYP27A1). The alternative pathway begins with converting cholesterol to (25R)-26-hydroxycholesterol by CYP27A1. Cytochrome P450 7B1 (CYP7B1) leads (25R)-26-hydroxycholesterol to CDCA. CDCA is converted to α-muricholic acid (MCA), and β-MCA. These BA are then conjugated with glycine or taurine. BA in rodents are also conjugated with taurine in the liver. BA synthesized in the liver are called primary BA. In the brain, 24S-hydroxycholesterol is converted from cholesterol by cytochrome P450 46A1 (CYP46A1). 24S-hydroxycholesterol is a precursor of 3β-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid, which can be converted to CDCA through the intermediates (3β, 7α-dihydroxy-5-cholenoic acid and 7α-hydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholenoic acid). A large amount of (25R)-26-hydoxycholesterol incorporates to brain from circulation, and (25R)-26-hydoxycholesterol can also be converted to 3β-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid.