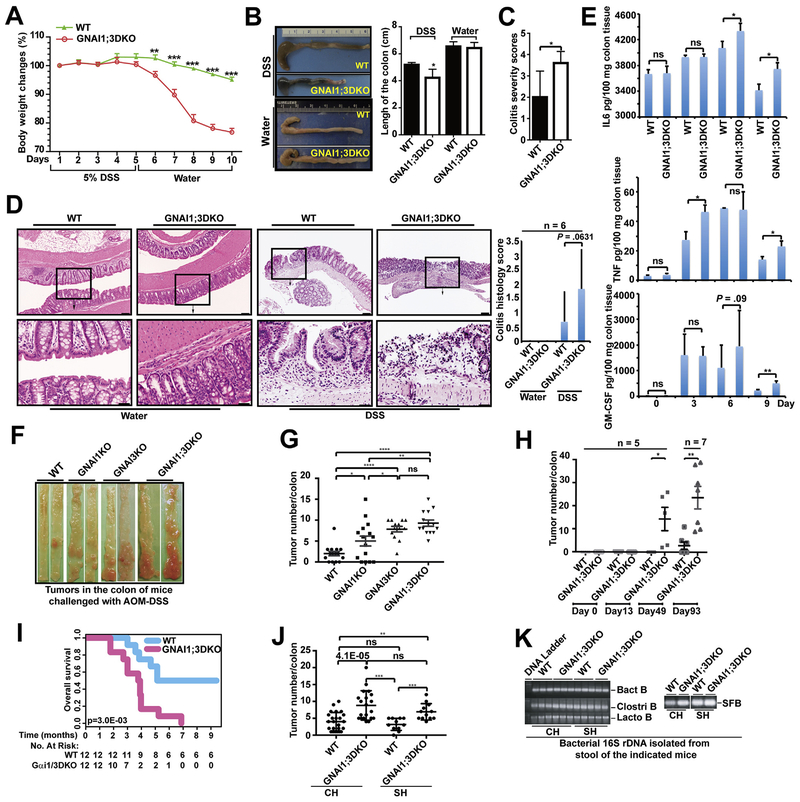
Figure 1.
GNAI1;3 inhibit colitis, and their ablation promotes the initiation and progression of CAC, which is independent of microbiota. (A) Body weight changes during the course of acute colitis with DSS (n = 6). (B) The change of colon length. (C) Colitis severity score. (D) H&E-stained representative images of the colons of WT and GNAI1;3DKO mice with histology score (n = 6) on day 10. Scale bars: upper, 100 μm; lower, 25 μm. (E) The levels of GM-CSF, IL6, and TNF in the supernatant of colon culture (n = 3). (F) Representative images of colonic tumors from WT and GNAI1;3DKO mice. (G) Tumor number/colon of WT (n 15), GNAI1KO (n = 15), GNAI3KO (n = 13), or GNAI1;3DKO (n = 14) mice. (H) number/colon of WT (n = 5) and GNAI1;3DKO (n = 5) on days 0,13,49 and WT (n = 7) and GNAI3 (n = 7) on day 93. (I) Overall survival of challenged WT andGNAI1;3DKOmice (n = 12/group).(J) Tumor number/colon of WT (n = 21) and GNAI1;3 DKO mice (n = 20) under the CH condition or WT (n = 11) and GNAI1;3 DKO mice (n = 12) under the SH condition. (K) Polymerase chain reaction analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA of the indicated bacteria in the stool isolated from the indicated mice. All analyzed data are mean ± standard error of the mean (A, G, and H) or standard deviation (B–E, J). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001; 2-tailed Student t test. Bact B, Bacteroides species; Clostri B, Clostridiales species; Lacto B, Lactobacillaceae species; ns, not significant; SFB, segmented filamentous bacteria species.