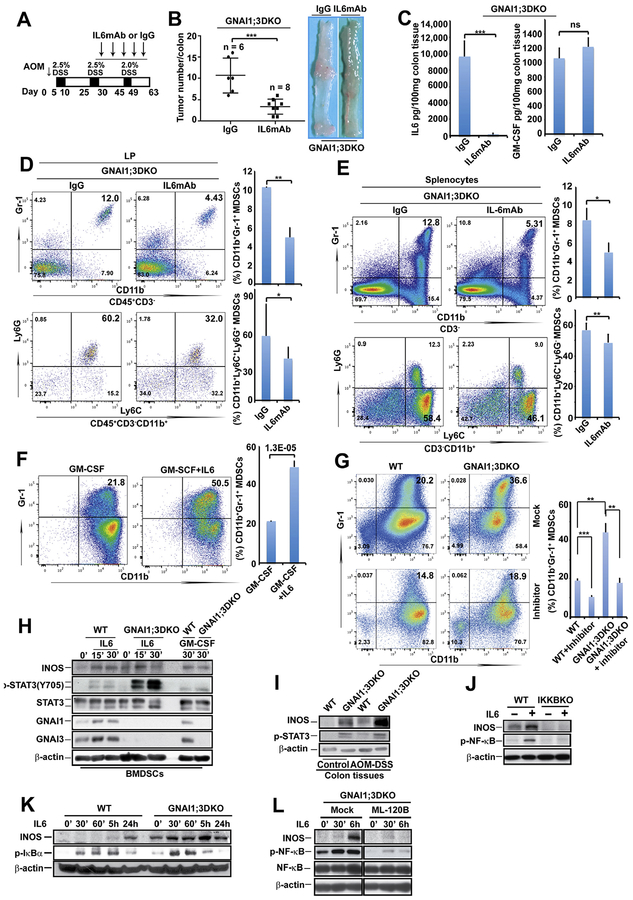
Figure 3.
IL6 mediates colitis-associated tumorigenesis and MDSC expansion in GNAI1;3DKO mice, and its activation of NF-ĸB and expansion of MDSCs are enhanced by GNAI1;3 deficiency. (A) Schematic intraperitoneal injection schedule of IL6 monoclonal antibody (IL6mAb) and its isotype immunoglobulin G control (IgG). (B) Left panel shows tumor number/colon of AOM–DSS-challenged mice with injection on day 63 (n = 6–8). Right panel shows representative images of colonic tumors of the mice. (C) Levels of IL6 and GM-CSF in the supernatant of colon culture from indicated mice in (B) (n = 3). (D, E) Representative FACS plots of CD45+CD3−CD11b+Gr-1+ and CD45+CD3–CD11b+Ly6G+ MDSCs in (D) the LP or (E) the spleen of the mice in part B (n = 3–6). (F) WT BMDSCs were differentiated by GM-CSF in the presence or absence of IL6 and then assayed for CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs (n = 3). (G) Representative FACS plots of CD11b+Gr-1+ BMDSCs of WT and GNAI1;3DKO mice (n = 3) differentiated with GM-CSF plus IL6 in the presence or absence of BP-1–102 (5 μmol/L) (left). Quantitative analysis of CD11b+Gr-1+ BMDSCs shown in the left panel is graphed on the right. (H) IB analysis for the levels of p-STAT3(Y705), STAT3, INOS, GN1AI, GNAI3, and β-actin in indicated WT and G GNAI1;3DKO BMDSCs. (I) IB analysis for expression of INOS, p-STAT3, and β-actin in the indicated mouse colonic tissues. (J) IB analysis for the levels of INOS, p-NF-ĸBp65(S536), and bactin in WT and IKKBKO MEFs. (K) IB analysis for the levels of INOS, p-IĸBα(S32), and β-actin in WT and GNAI1;3DKO MEFs. (L) IB analysis for the levels of INOS, p-NF-ĸBp65(S536), NF-ĸB, and β-actin in GNAI1;3DKO MEFs in the presence or absence of ML-120. Data are mean ± standard deviation. **P < .01, ***P < .001, 2-tailed Student t test. Except in A–E, all data are representative of 2 or 3 independent experiments. mAb, monoclonal antibody; p-, phosphorylated.