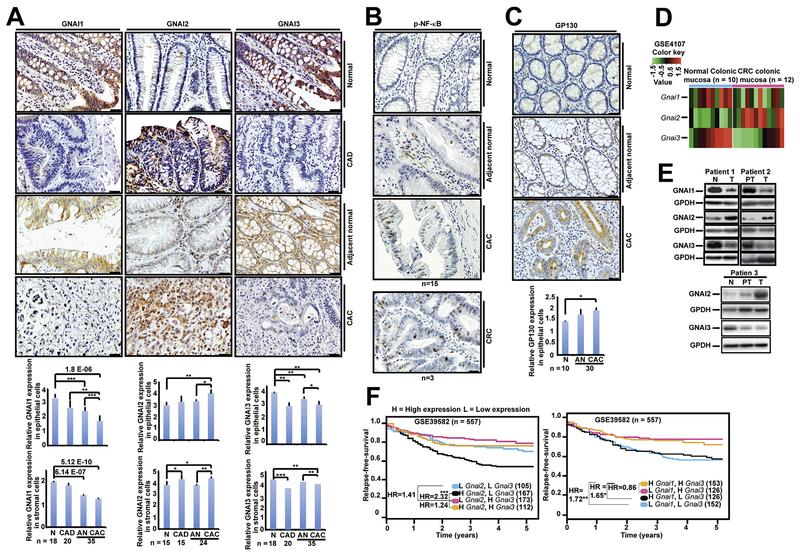
Figure 7.
Low GNAI1;3 expression and high GNAI2 expression are associated with colorectal tumorigenesis and poor patient survival. (A–C) IHC staining for (A) GNAI1-, GNAI2-, and GNAI3-, (B) p-NF-ĸBp65(S536)–, and (C) GP130-positive cells in the normal, dysplastic (CAD), and adjacent nonneoplastic or neoplastic (CAC) epithelial cells and corresponding surrounding stromal cells. Quantitative analyses of GNAI1, GNAI2, GNAI3, and GP130 are shown under the images. All data are mean ± standard deviation. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001; 2-tailed Student t test. Scale bars: 25 mm. (D) Heatmap analysis of GSE4107 CRC mucosal tissue DNA microarray for expression of Gnai1, Gnai2, and Gnai3 mRNA. (E) IB analysis for GNAI1, GNAI2, or GNIA3 in CRC patients’ normal colon (N), peritumor (PT), or tumor (T) tissues. (F) Relapse-free survival of 4 subgroups of CRC patients classified by different combinations of Gnai1 and Gnai3 expression levels (left) and Gnai2 and Gnai3 expression levels (right).