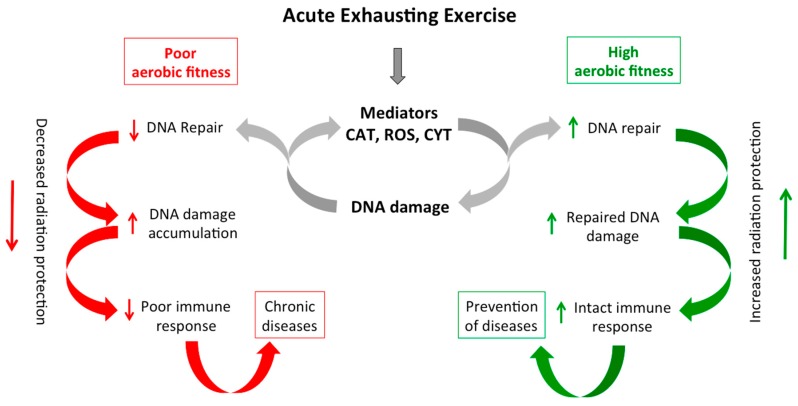
Figure 6.
Cellular consequences of acute exhausting exercise in immune cells. One bout of acute exhaustive exercise induces DNA damage through mediators such as catecholamines (CAT), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and/or cytokines (CYT). Immune cells from individuals with poor aerobic fitness have a limited DNA repair capacity leading to accumulation of DNA damage and consequently a poor immune response (red arrows), while immune cells from individuals with a high aerobic fitness have an enhanced DNA repair capacity protecting immune system and therefore preventing the onset of diseases (green arrows).