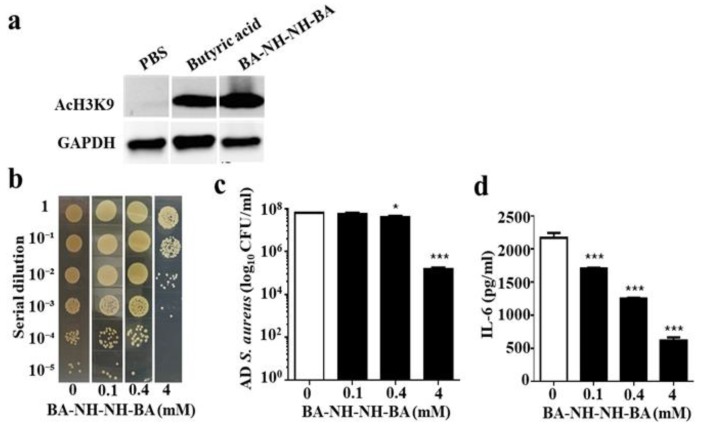
Figure 6.
Induction of histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (AcH3k9) and reduction of AD S. aureus growth and IL-6 production by BA–NH–NH–BA. (a) Human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT) were treated with 4 mM butyric acid or BA–NH–NH–BA in PBS for 8 h. Cells treated with PBS served as a control. The presence of AcH3K9 in cells was detected by Western blotting using an anti-AcH3K9 antibody. A representative result from three similar experiments is shown. (b) A 1 cm wound was made on the dorsal skin of ICR mice before applying AD S. aureus with PBS alone (0 mM) or BA–NH–NH–BA (0.1-4 mM in PBS) for 3 d. Bacterial CFUs in the skin wounds were enumerated by plating serial dilutions of the homogenate on a plate. The number (log10 CFU/mL) of AD S. aureus bacteria (c) and the level of IL-6 pro-inflammatory cytokine (d) were determined. Data are the mean ± SE of three separate experiments. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 (two-tailed t-tests).