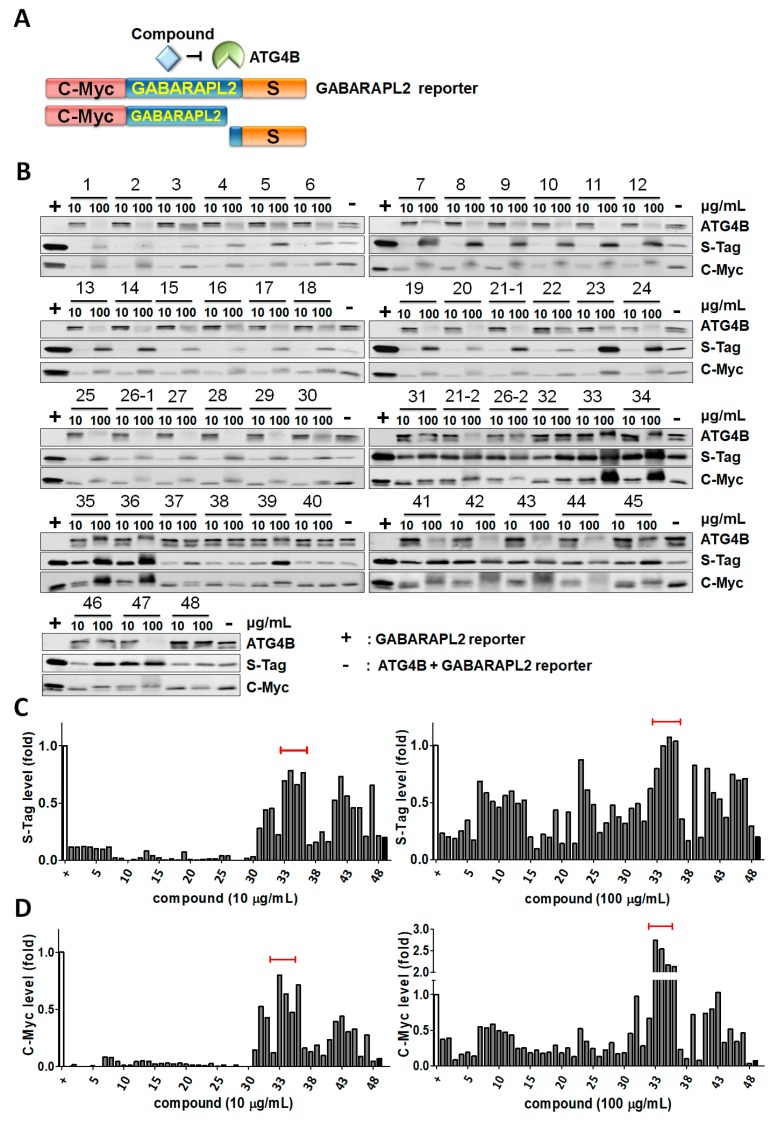
Figure 1.
Screening for ATG4B inhibitors with medicinal plants using ATG4B cleavage assays. (A) Schematic diagram for the biochemical reaction to measure ATG4B proteolytic activity. Briefly, the substrate GABARAPL2 fused with the N-terminal C-myc tag and C-terminal S-tag. If extracts inhibited ATG4B, both full-length C-myc-tagged GABARAP2 (upper band) and a short peptide of S-tag can be detected by immunoblotting. (B) Recombinant ATG4B (5 nM) was mixed with the GABARAPL2 fusion protein (1 μM) in a reaction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-base, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, and 1 mM DTT with 10-fold diluted formosan plant extracts (10 or 100 μg/mL). The retained S-tag and full-length C-myc tag (upper band) were determined by immunoblotting. The reactions without (+) and with (−) recombinant ATG4B were used as positive and negative controls of inhibition, respectively. (C) The protein levels of S-tag and (D) full-length C-myc-tagged GABARAPL2 were quantitated by ImageJ and normalized by positive control (+) as 100% inhibition of ATG4B in each blot.