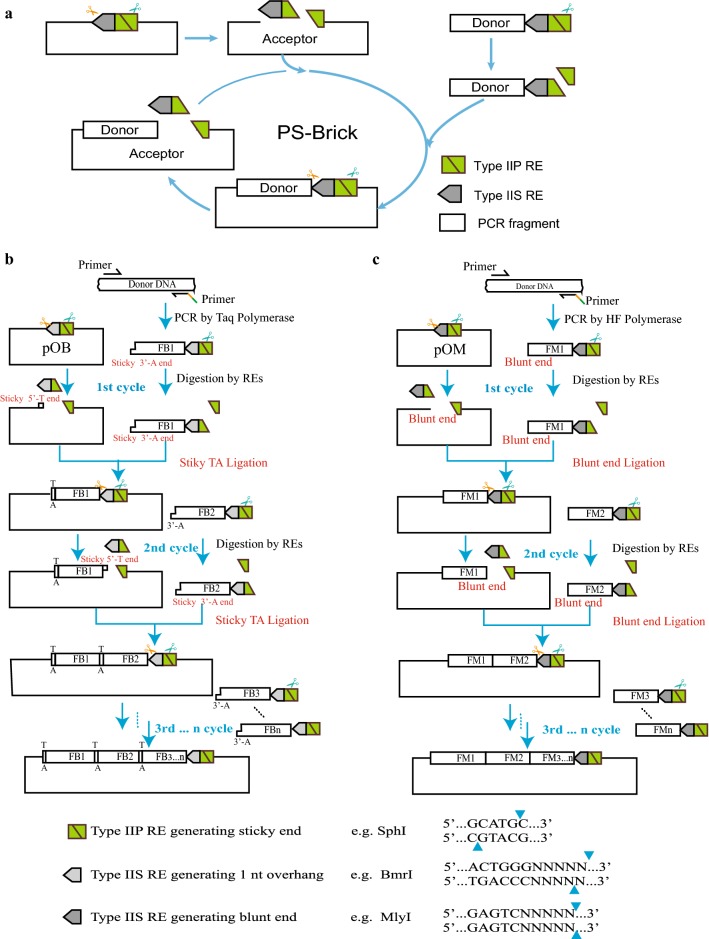
Fig. 1.
The PS-Brick design and workflow. a The overall cycle of the PS-Brick assembly method. b Strategy of BmrI based TA cloning. The original PS-Brick vectors pOB containing the entrance sites of adjacent SphI/BmrI were double digested using the corresponding RE pair. The recognition sites of BmrI and half of SphI recognition site were detached, leaving behind one 1-nt cohesive end generated by BmrI and the 4-nt cohesive end generated by SphI. The PCR products amplified by Ex-Taq DNA Polymerase and monoterminally flanked by SphI/BmrI were digested by only SphI, and then linked to the 4-nt complementary cohesive end of the digested vector backbones. Meanwhile, the other end of the digested vector backbones with 1-bp cohesive end was linked with non-cut end of the PCR products through TA cloning. c Strategy of MlyI based blunt end ligation. The original PS-Brick vectors pOM containing entrance site of adjacent SphI/MlyI were double digested using the corresponding RE pair. The recognition site of MlyI and half of SphI recognition site were detached, leaving behind a blunt end generated by MlyI and a 4-nt cohesive end generated by SphI. The PCR products amplified by Kappa high-fidelity polymerase monoterminally and flanked by SphI/MlyI were digested by only SphI, and then linked to the 4-nt complementary cohesive end of the digested vector backbones. Meanwhile, the other end of the digested vector backbones with blunt end was linked with non-cut end of the PCR products through blunt end ligation. The newly assembled vectors once again contains the same entrance sites of adjacent SphI/BmrI or SphI/MlyI and could therefore be used for next round of parts incorporation. FB and FM denote the donor PCR fragments for PS-Brick assembly with entrance sites SphI/BmrI and SphI/MlyI, respectively