Figure 1. Structure of the ErbB Receptor.
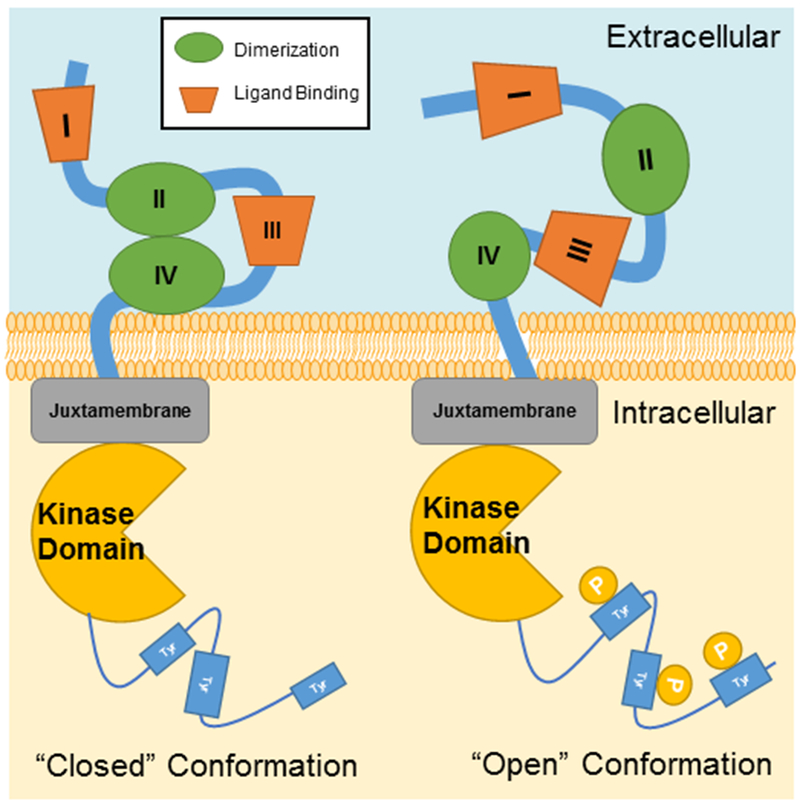
ErbB receptors transmembrane proteins with both intracellular and extracellular domains. The extracellular domain is composed of four sub-domains, including two leucine-rich sub-domains (I and III) for ligand binding and two cysteine-rich sub-domains (II and IV) for dimerization with activated ErbB members. Inactivated ErbB receptors remain in the ‘closed’ conformation, while ErbB-2 is constitutively in the ‘open’ confirmation. The dimerization with other ligand-bound ErbB family members will lead to activate ErbB-2 for signaling. Intracellularly, ErbB receptors have a juxtamembrane region, a kinase domain, and a cytoplasmic tail that is regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation.
