Figure 1.
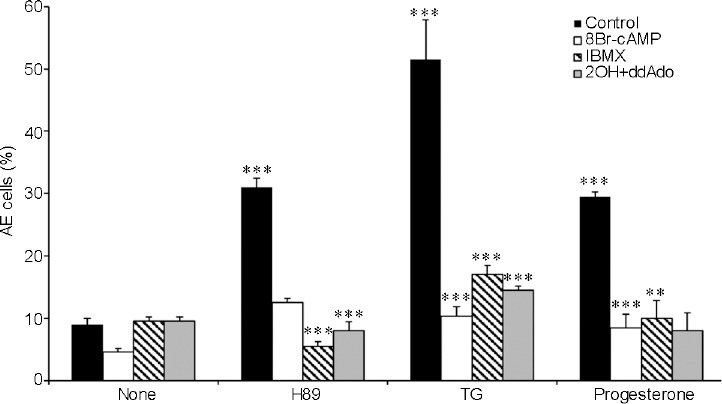
Effect of protein kinase A inhibition and 8-bromo-cAMP (8Br-cAMP) on AE. After 160 min of incubation (Control), 0.1 mmol l−1 (8Br-cAMP), 0.5 mmol l−1 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine (IBMX), or 20 μmol l−1 hydroxy-2-methylpropiophenone (2-OH-estradiol) + 100 μmol l−1 2'5'-dideoxyadenosine (2OH+ddAdo) (sAC/tmAC inhibitors) were added. The AE inducers are: N-[2-(p-Bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5isoquinolinesulfonamide (H89; 50 μmol l−1), TG (3 μmol l−1), progesterone (5 μmol l−1) or antibiotic A23187 calcium ionophore (A23187; 10 μmol l−1). The values shown represent the mean ± standard deviation of duplicates from three experiments from three different donors. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, significant difference compared to the corresponding control. cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; AE: acrosomal exocytosis; sAC: soluble adenylyl cyclase; tmAC: transmembrane adenylyl cyclase; TG: thapsigargin.
