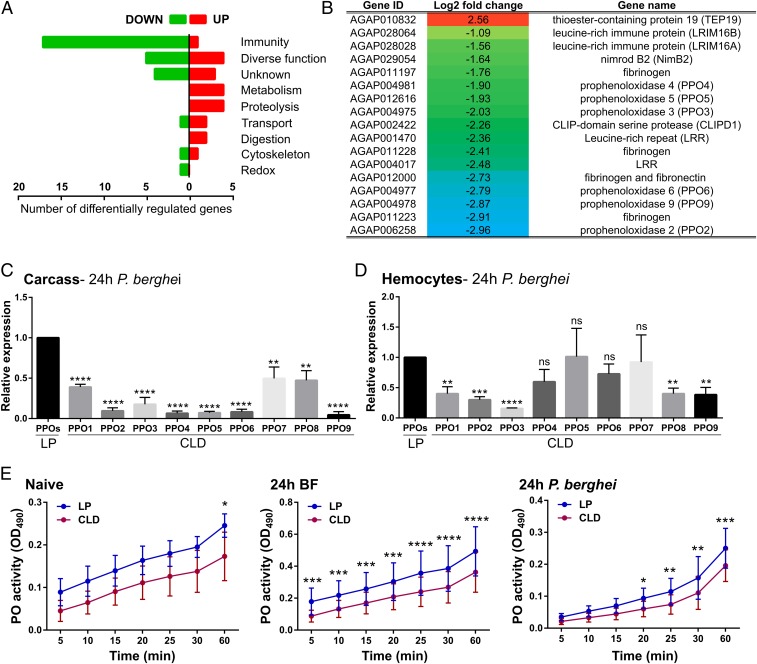
Fig. 4.
Phagocyte depletion reduces of prophenoloxidase (PPO) expression. RNA-seq analyses following clodronate treatment revealed 50 differentially regulated genes in abdomen tissues 24 h post-P. berghei infection and grouped by gene ontology (A). Comprising the largest category of affected genes, the annotations and logtwofold change of specific immune genes with significant differential regulation are displayed (B). This includes several PPO genes, therefore leading us to examine the expression of all 9 PPO family members by qRT-PCR analyses in the carcass (C) and hemocyte (D) samples in control liposome (LP) and clodronate-treated (CLD) samples. Data were analyzed using an unpaired t test to determine differences in relative gene expression of each respective PPO gene between LP and CLD treatments (C and D). Due to the importance of PPOs in phenoloxidase (PO) activation, PO activity was measured in hemolymph samples derived from LP and CLD samples in naive, blood-fed, and P. berghei-infected conditions (E). Measurements (OD490) were taken for DOPA conversion assays at 5-min intervals from 0 to 30 min, and then again using a final readout at 60 min. Data were analyzed using a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons using GraphPad Prism 6.0. Bars represent mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. Asterisks denote significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).