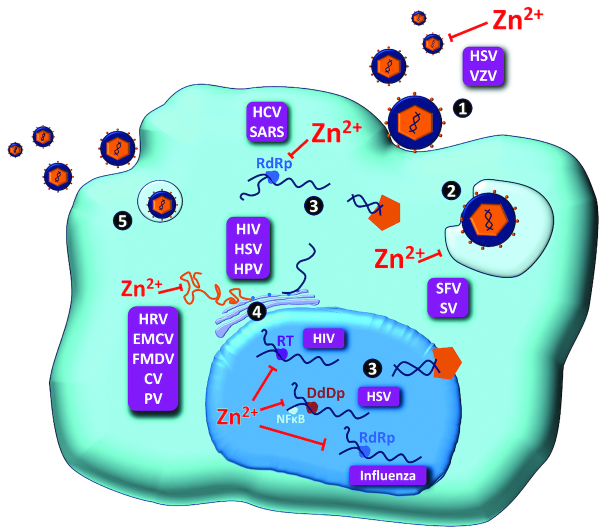
FIGURE 1.
The diverse stages of viral replication cycles that are inhibited by zinc. In vitro studies have demonstrated a number of mechanisms by which zinc interferes with the viral replication cycle. These include free virus inactivation (1), inhibition of viral uncoating (2), viral genome transcription (3), and viral protein translation and polyprotein processing (4). No studies to date, however, have demonstrated zinc-mediated inhibition of virus assembly and/or particle release. CV, coronavirus; DdDp, DNA-dependent DNA polymerase; EMCV, encephalomyocarditis virus; FMDV, foot and mouth disease virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HPV, human papilloma virus; HRV, human rhinovirus; HSV, herpes simplex virus; PV, polio virus; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RT, reverse transcriptase; SARS, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; SFV, Semliki Forest virus; SV, sindbis virus; VZV, varicella-zoster virus; Zn, zinc.