Fig. 1. Stability analysis of the human HMCES SRAP-abasic site DNA protein crosslink.
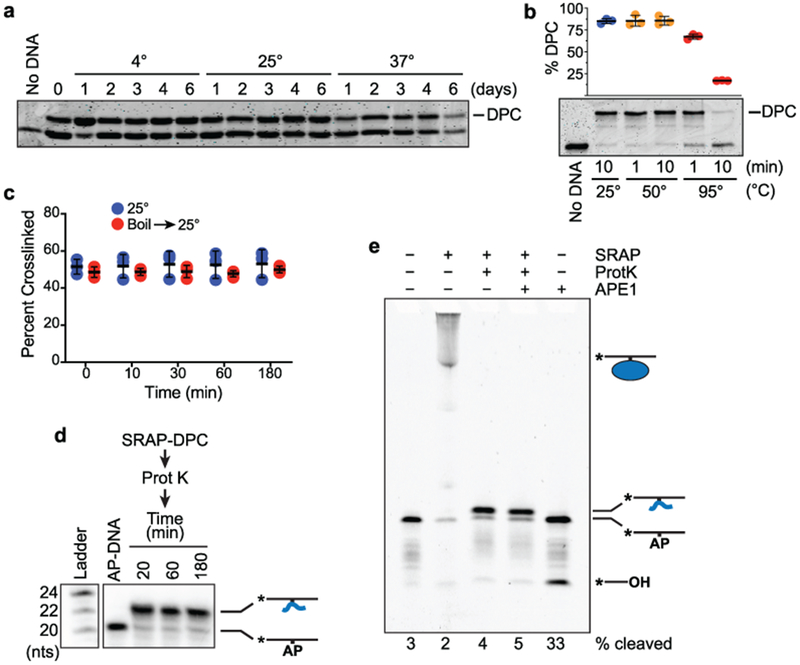
a, HMCES SRAP DPC stability measured at the indicated temperatures. Free and DNA-crosslinked HMCES was detected by coomassie blue staining. The HMCES-DPC percentage in this experiment is approximately 50% because uncrosslinked DNA was removed by dialysis after a short reaction time. b, Boiling the HMCES DPC causes hydrolysis (mean ± S.D., n=3 independent measurements) c, HMCES DPC stability measured before or after denaturation by boiling for two minutes. d, HMCES SRAP domain was incubated with a 20-mer AP-site containing oligonucleotide to form a crosslink, digested with proteinase K followed by heat inactivation of the protease, and then incubated at 37°C for the times indicated. Electrophoresis and autoradiography was used to visualize the DNA. e, HMCES SRAP was incubated with 31-mer AP-DNA and digested with proteinase K, and the peptide DPC incubated with APE1 for 2 hours. Bands were visualized by Cy5 fluorescence. Uncropped gel images are shown in Supplementary Data Set 1. Source data for b,c are available online.
