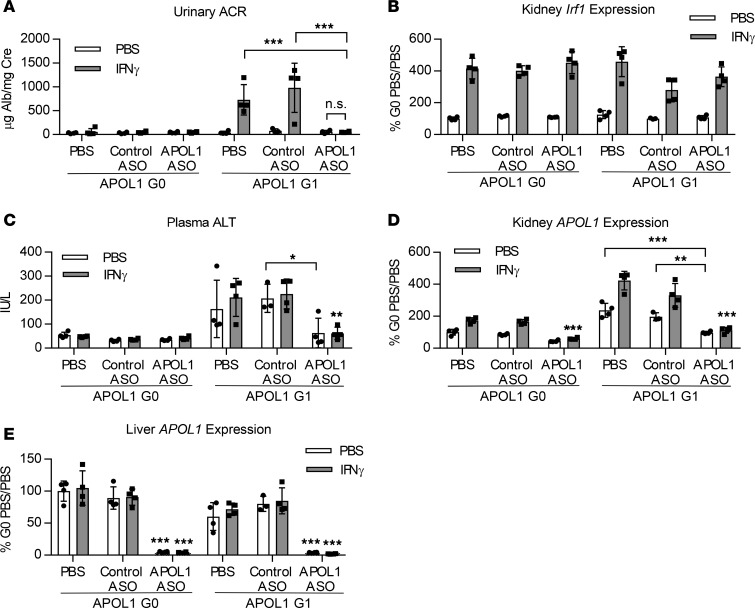
Figure 5. Administration of IONIS-APOL1Rx prevents IFN-γ–induced proteinuria.
Female APOL1 G0– and G1–transgenic mice (n = 3–4) were treated with 50 mg/kg IONIS-APOL1Rx or control ASO 1 time per week for 4 weeks and challenged with a single dose of IFN-γ (1.125 × 107 U/kg) or vehicle (PBS). Study endpoints were evaluated 48 hours after IFN-γ challenge. (A) Urine was collected prior to sacrifice 48 hours after IFN-γ challenge, and urinary albumin was measured by ELISA and normalized to urine creatinine. (B) Kidney Irf1 expression was measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to Cyp expression. (C) Plasma ALT levels were measured using a clinical chemistry analyzer. (D) Kidney and (E) liver APOL1 expression were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to Cyp expression. All data are presented as mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Unless otherwise indicated, similar statistical significance was achieved when comparing APOL1 ASO–treated groups challenged with PBS or IFN-γ in comparison to respective PBS- or control ASO–treated groups.