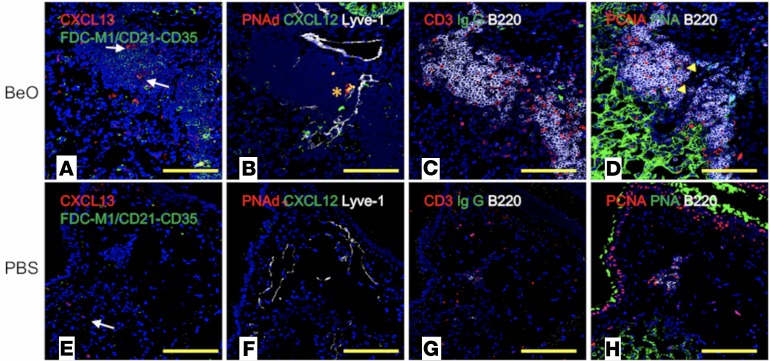
Figure 3. BeO exposure of HLA-DP2–Tg mice induced the formation of ectopic lymphoid aggregates (ELAs).
Representative multicolor immunofluorescence lung images of serial sections from HLA-DP2–Tg mice exposed to either BeO (A–D) or PBS (E–H) are shown. Original magnification, ×200. (A and E) Lung sections were stained for CXCL13 (red), FDC-M1 (green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (A) FDC-M1+ cells with branched stromal cell morphology were not present; however, CXCL13+ cells with stromal cell morphology (white arrows) were located inside lymphoid aggregates of BeO-exposed mice. (E) CXCL13+ cells with monocyte/macrophage–like morphology (white arrows) were present in PBS-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice in the absence of ELAs. (B and F) Lung sections were stained for expression of CXCL12 (green), PNAd/high endothelial venule (HEV) cells (red), lymphatic vessels/Lyve-1 (white), and with DAPI (blue). (B) ELAs with CXCL12+ (green) PNAd+ HEVs (orange asterisk), and Lyve-1+ lymphatics were present in BeO-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice. (F) A small PNAd+ HEV and Lyve-1+ lymphatics in PBS-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice are shown. (C and G) Lung sections were stained for expression of IgG (green), CD3 (red), B220 (white), and with DAPI (blue). (C) CD3+ T cells outside and inside of B220+ B cell aggregates in the lungs of BeO-treated HLA-DP2–Tg–mice are shown. (G) Few dispersed B220+ B cells and CD3+ T cells were seen in the PBS-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice. (D and H) Lung sections were stained for expression of PCNA (red), PNA (green), B220 (white), and with DAPI (blue). (D) Large B cell blasts (PCNA+PNA+B220lo, yellow arrowheads) were present in B cell aggregates of BeO-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice. (H) Rare B220+ B cells were seen in the small ELAs observed in PBS-treated HLA-DP2–Tg mice and were not expressing PCNA or PNA. Yellow scale bars: 100 μm.