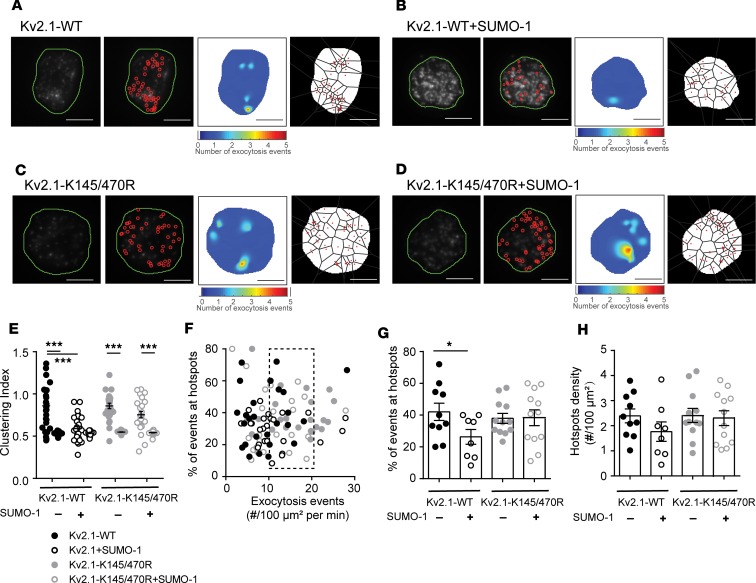
Figure 8. Kv2.1 SUMOylation sites regulate compartmentalization of fusion events.
(A–D) Example fusion events tracked by TIRF imaging of NPY-EGFP expression shown individually (red circles), as density heatmaps, or separated by Voronoi polygons in ND β cells expressing Kv2.1-WT (A) alone or (B) with SUMO1 and Kv2.1-K145/470R (C) alone or (D) with SUMO1. Scale bars: 5 μm. (E) Uniformity index values calculated from Voronoi polygons show that SUMO1 reduces the compartmentalization of fusion events in cells expressing Kv2.1-WT but not the SUMOylation-deficient mutant Kv2.1-K145/470R (n = 10, 8, 12, and 12 cells from 4 donors). (F) Scatter plot showing the relationship between proportion of events occurring within hotspots versus event frequency. A subset of cells (dashed box) was chosen for further analysis. (G and H) SUMO1 reduced the proportion of events occurring at (G) hotspots with little effect on (H) the overall hotspot density. Significance was determined by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s posttest. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.