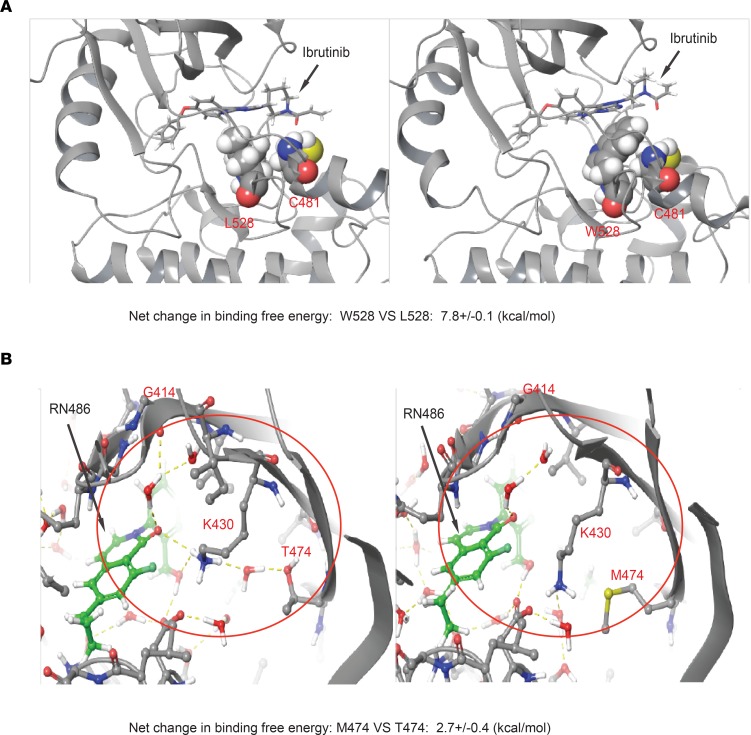
Figure 3. Structural modeling of the binding to BTK L528W and T474M mutants.
(A) The structural context of ibrutinib binding in BTK W528 compared with L528. The BTK protein is shown in cartoon representation. Ibrutinib and its covalent attachment point C481, as well as L528/W528, are highlighted in all-atom CPK representation. The mutation of L528 to W528 sterically destabilizes interactions of ibrutinib with C481. (B) Structural modeling of wild-type BTK (T474) and BTK T474M mutation (M474) binding to RN486. The H-bonded network involving K430, T474, and G414 backbone is shown in yellow dotted lines and highlighted within the red circle. This water network is disrupted by the mutation of T474 to M474.