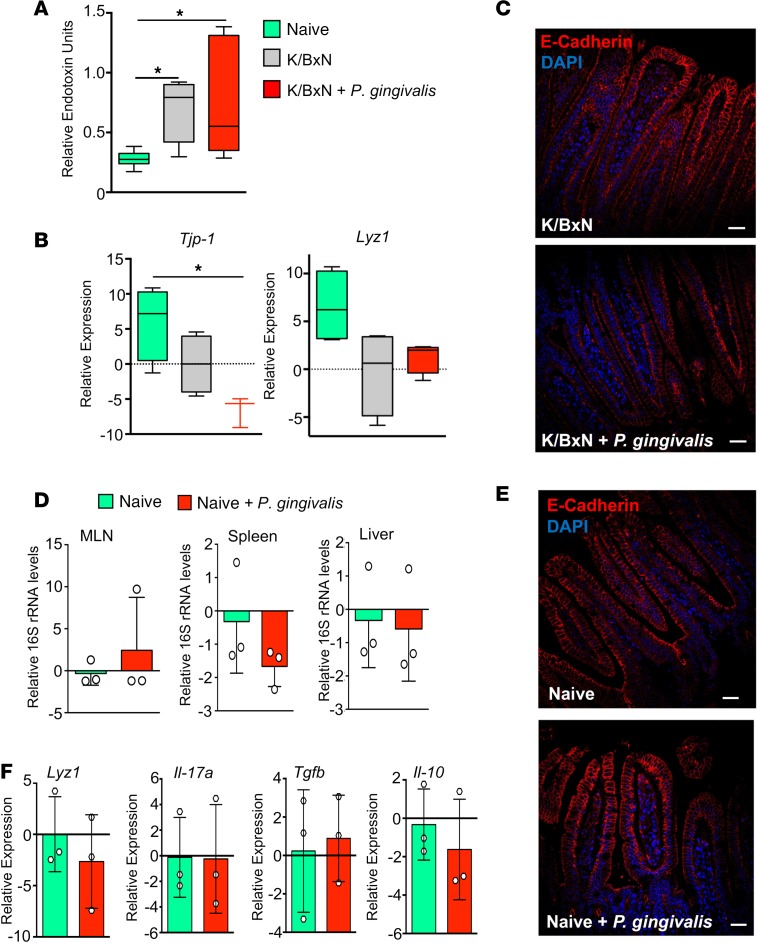
Figure 1. Inoculation of arthritic but not naive mice with P. gingivalis promotes gut barrier breakdown.
(A–C) Mice were inoculated with P. gingivalis (109 CFU per mouse) or given vehicle (PBS) on days –1, 1, and 3 and injected with K/BxN serum (50 μL per mouse, i.p.; days 0 and 2). Tissues were harvested on day 8 after K/BxN administration, and (A) plasma endotoxin concentrations were determined. (B) Gene expression of tight junction protein Tjp1 and antimicrobial Lyz1. Results for A and B are mean ± SEM. n = 3–4 mice per group from 2 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 using Kruskall-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test. (C) Representative images of E-cadherin staining in arthritic mice (K/BxN) inoculated with or without P. gingivalis (scale bars: 25 μm). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 4 mice per group from 2 independent experiments. (D) Mice were gavaged with P. gingivalis (109 CFU, days –1, 1, 3) or vehicle. 16S rRNA gene levels were measured by 16S qPCR in mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs), spleens, and livers of naive control mice or P. gingivalis–inoculated mice (Naive + P. gingivalis) to assess breach of bacteria across the gut barrier. Results are mean ± SEM for n = 3 mice per group; unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. (E) Representative images of E-cadherin (red) and DAPI staining (blue) of ileal tissue from naive mice or P. gingivalis–inoculated mice (Naive + P. gingivalis). Representative of n = 4 mice from 2 independent experiments. Scale bars: 25 μm. (F) Gene expression levels of intestinal epithelium–secreted antimicrobial Lyz1 and cytokines Il17a, Tgfb, and Il10 in intestines of naive and nonarthritic P. gingivalis–inoculated (Naive + P. gingivalis) mice. Results are mean ± SEM for n = 3 mice per group.