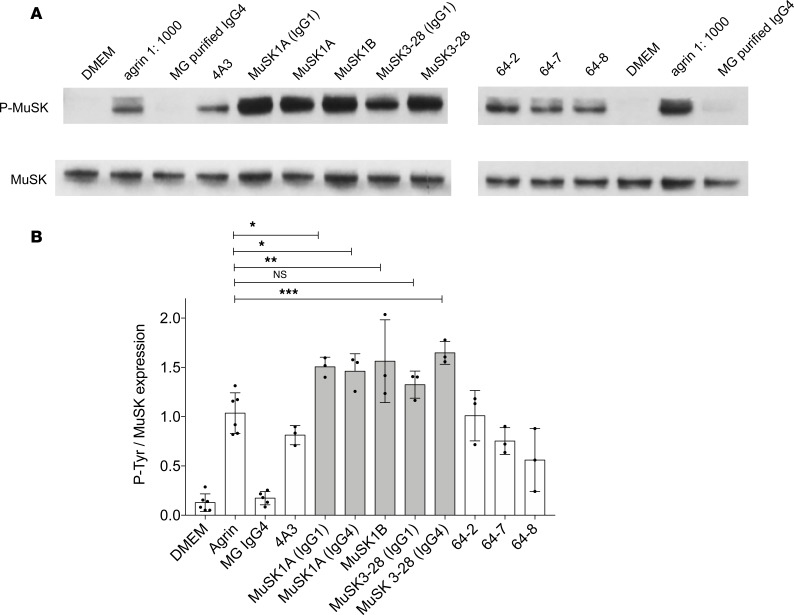
Figure 5. MuSK mAbs can amplify agrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation.
(A) Immunoblots showing phosphotyrosine bands and related MuSK expression in C2C12 murine myotubes that were incubated with agrin in the presence of MuSK MG serum-derived IgG4 or recombinant MuSK/control mAbs. 4A3 is a humanized murine MuSK mAb; MuSK1A, MuSK1B, and MuSK3-28 are human MuSK mAbs from patients with MuSK MG; and 64-2, 64-7, and 64-8 are non–MuSK-binding human mAbs derived from AChR MG patient plasmablasts. IgG4 subclass mAbs MuSK1A and MuSK3-28 were expressed in vectors reflecting the native subclass and as IgG1 (as indicated). (B) Normalized densitometry analysis results from the MuSK phosphorylation immunoblots are plotted. Each data point represents an independent experiment. Bars represent means and error bars SDs. Phosphorylation of MuSK was determined by normalizing to MuSK expression, detected by a commercial anti-MuSK antibody after stripping the blot, and the ratio of phosphotyrosine MuSK/MuSK is plotted. Multiple-comparisons ANOVA (versus agrin), Dunnett’s test; ns P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, shown for MuSK mAbs versus agrin comparisons.