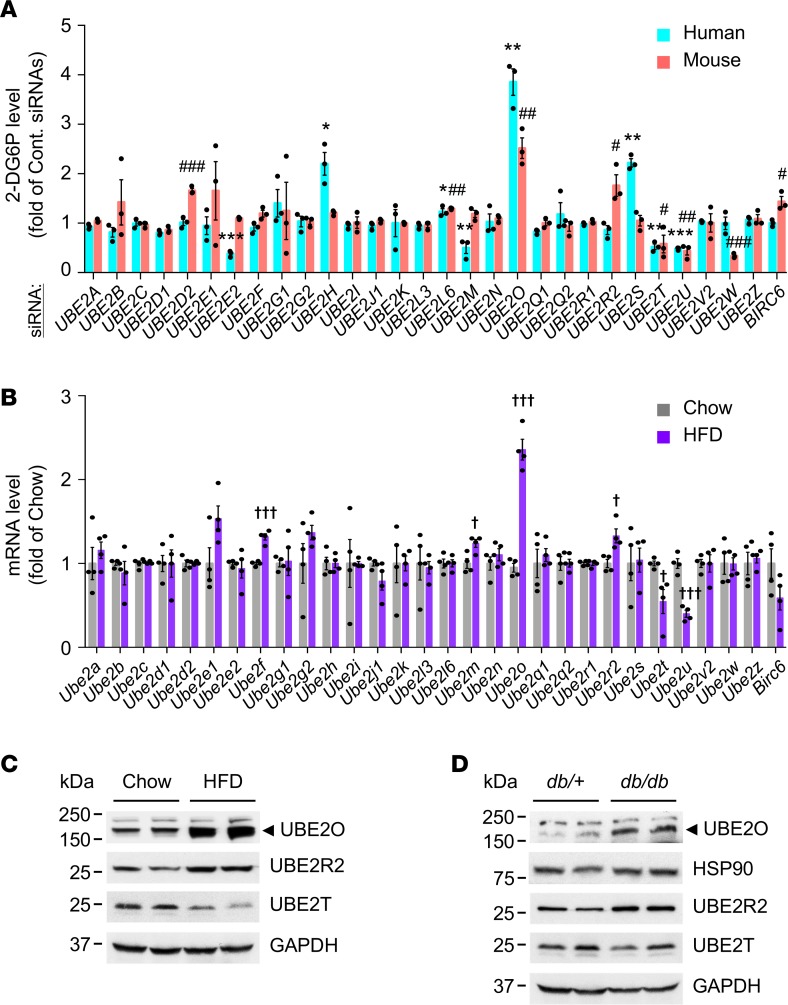
Figure 1. UBE2O is upregulated in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes.
(A) An RNA interference (RNAi) screen identifies UBE2O as a potent regulator of glucose uptake in myotubes. Primary normal human skeletal myotubes (HSkMs) and C2C12 mouse myotubes expressing a nontargeting control siRNA pool (Cont. siRNAs) or a synthetic siRNA library targeting 30 human and mouse E2s, respectively, were subjected to a screen for insulin-stimulated 2-deoxyglucose uptake. 2-DG6P, 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate. n = 3. (B) Total RNAs from quadriceps skeletal muscles of mice fed a normal chow or an HFD for 28 weeks were subjected to RT-qPCR. n = 4. (C and D) Lysates from quadriceps skeletal muscles of 9-month-old Ube2o+/+ mice fed normal chow or an HFD for 28 weeks (C) and 25-week-old type 2 diabetic db/db and lean (db/+) mice (D) were subjected to immunoblotting. Error bars represent ±SEM. P value was determined by Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, control siRNAs HSkMs vs. E2 siRNAs HSkMs; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, control siRNAs C2C12 vs. E2 siRNAs C2C12; †P < 0.05, †††P < 0.001, chow vs. HFD. Uncropped gels and blots are available in the supplemental material.