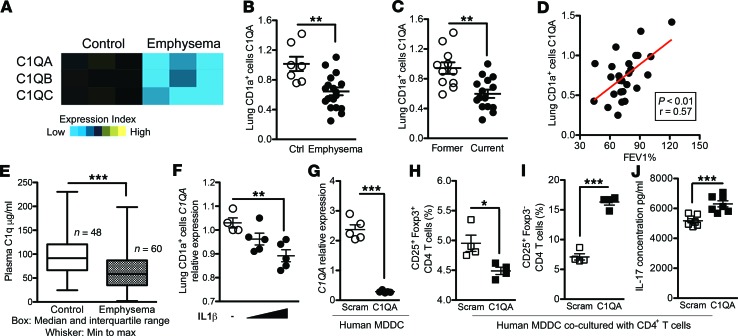
Figure 1. mRNA expression and protein concentration of C1q are reduced in human emphysema.
(A) Heatmap using microarray of C1q expression in lung CD1a+ cells isolated from control and emphysema patients (GSE26296). (B) Expression of C1QA mRNA in CD1a+ APCs isolated from total lung cells was measured by qPCR (normalized to 18S expression). Ctrl, control (smokers without emphysema); N = 26. (C) The same data were used to separate subjects based on current (active) vs. former (>1 year inactive) smoking history. **P < 0.01. (D) Linear regression was used to find the correlation between C1QA mRNA in CD1a+ APCs and airway obstruction as measured by lung function (% forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FEV1). (E) Plasma samples from control (n = 48) and emphysema patients (n = 60) were used to measure C1q concentration using ELISA. Box, median and interquartile range; whiskers, min to max range. ***P < 0.001. (F) Human CD1a+ lung cells isolated by autoMACS were cultured in complete medium (RPMI-1640 with 10% FBS and Pen-Strep) at a concentration of 1 × 106/mL and treated with increasing concentration of purified human IL-1β (100 pg/mL, 1 ng/mL) for 48 hours or with medium alone as the vehicle. The expression level of C1QA was measured by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qPCR). (Normalized to 18S expression). n = 3; *P < 0.05. Results are represented as mean ± SEM, from 3 independent experiments. (G) Knockdown of C1QA expression in human cDCs was achieved by transfection of C1QA-specific siRNA. Scrambled siRNA was transfected as a control. The expression of C1QA mRNA was measured by qPCR (Normalized to 18S expression). ***P < 0.001. (H and I) CD4+ T cells isolated from PBMCs were cocultured with allogeneic APCs shown in 10:1 ratio (CD4+ T cells and APCs) for 3 days, and CD25+Foxp3+ (H) and CD25+Foxp3– (I) T cell population were measured using flow cytometry. ***P < 0.001. (J) The concentration of IL-17A in the supernatant from cell cultures in (I) was measured by multiplex assay. ***P < 0.001. P values were determined by the Mann-Whitney nonparametric test.