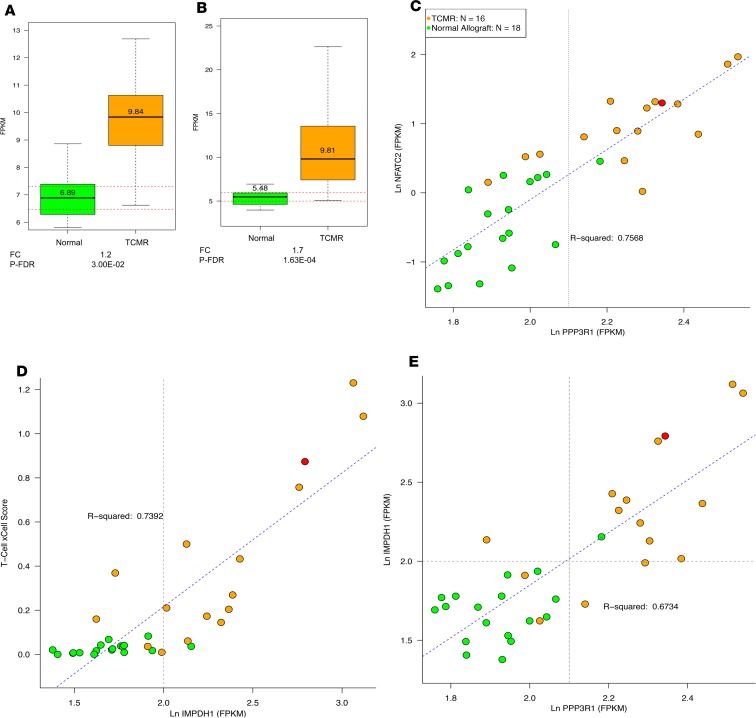
Figure 8. Kidney allograft expression of mRNAs encoding calcineurin PPP3R1 and inosine-5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1 (IMPDH1) in TCMR and Normal.
Intragraft mRNA abundance of calcineurin isoform PPP3R1 (protein phosphatase 3 regulatory subunit B, α) (A), and IMPDH1 (B) in TCMR and Normal. In the box plots, the 2 dotted red lines represent the 95% confidence interval of the Normal group. Calcineurin, a phosphatase made of 2 proteins, CNA and CNB, cleaves phosphate from serine and threonine in proteins. CNA possesses the phosphatase enzymatic activity and binds calmodulin. CNB binds Ca2+ directly and regulates the activity of CNA. Tacrolimus acts as an immunosuppressive drug by binding to and inhibiting calcineurin. We used PPP3R1 mRNA abundance as a marker of calcineurin inhibition. Mycophenolate acts by inhibiting IMPDH, an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of inosine monophosphate to xanthosine monophosphate, which is the rate-limiting step in the de novo biosynthesis of guanine nucleotide. We used IMPDH1 mRNA abundance as a marker of mycophenolate action. Scatter plots depict the association between calcineurin isoform PPP3R1 and NFATC2, a key transcription factor necessary to produce the T cell proliferative cytokine IL-2 (C), between IMPDH1 and a T cell score derived by xCell (D), and between PPP3R1 and IMPDH1 (E). We used NFATC2 as a marker of the effect of calcineurin inhibition on T cells. We used T cell xCell score as a marker of the effect of mycophenolate on T cells. One patient in the TCMR group who did not receive tacrolimus is shown in red in the scatter plot.