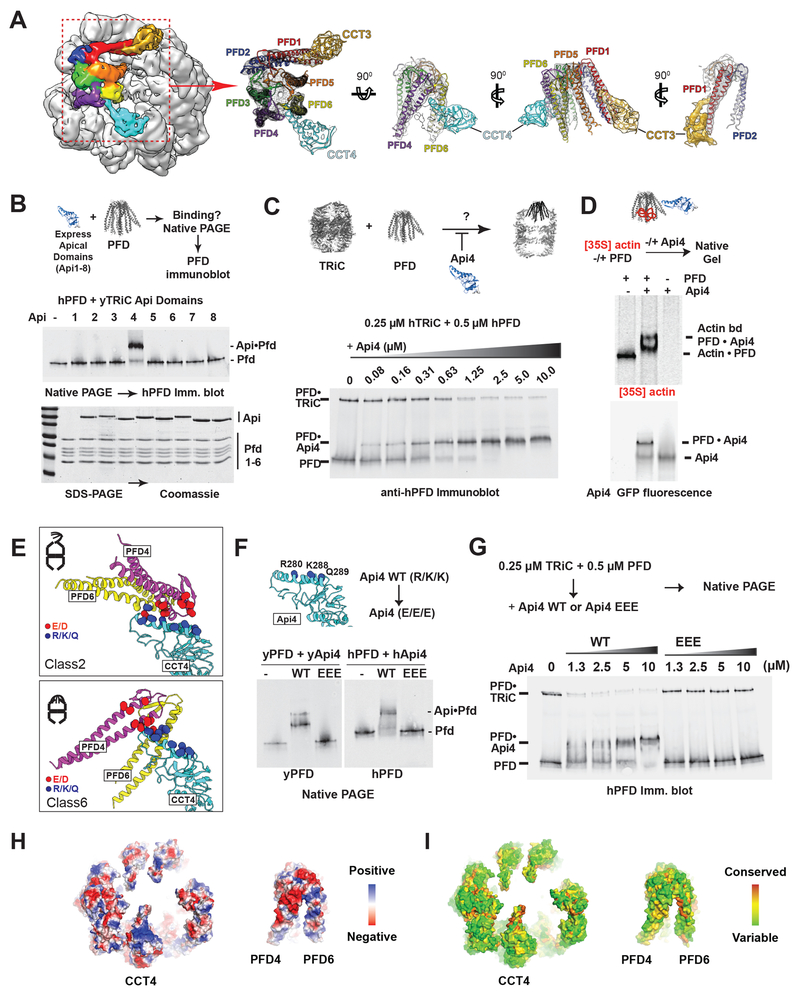
Figure 6. TRiC–PFD interaction site mediated by an electrostatic pivot point on CCT4.
(A) CryoEM map of Class 6 highlighting the PFD and TRiC interaction. Segmented map with fitted model showing the direct contact of PFD to apical helix of CCT4 (Cyan) and 5 (Gold). (B) Binding of purified CCT apical domains to PFD analyzed by NPAGE and immunoblot for PFD. (C) Competitive inhibition of TRiC–PFD binding by apical domain of CCT4 (Api4), analyzed by NPAGE and immunoblot. TRiC binding to PFD is inhibited at near equimolar concentrations of Api4. (D) 35S-Actin binding to PFD alone, PFD with Api4, and Api4 alone analyzed by NPAGE followed by fluorescence and autoradiography. (E) Api4–PFD interface highlighting positive charges in Api4 (blue) and negative charges in PFD (red). (F) TRiC–PFD binding is not competed away by Api4–EEE mutant (Yeast: R268E, K276E and K277E, Human: R280E, K288E, Q289E), but is competed away by WT Api4 (G); indicating loss of Api4-EEE binding to PFD. (H) Model of hTRiC and hPFD interface between Pfd4 and Pfd6 and TRiC: electrostatics modeled in blue to red color gradient indicating positive to negative charge. (I) Surface conservation of TRiC and PFD interface obtained from alignment of 100 orthologous sequences mapped onto the hTRiC and hPFD structures. Color gradient of red to green indicates decreasing conservation.