Fig. 3.
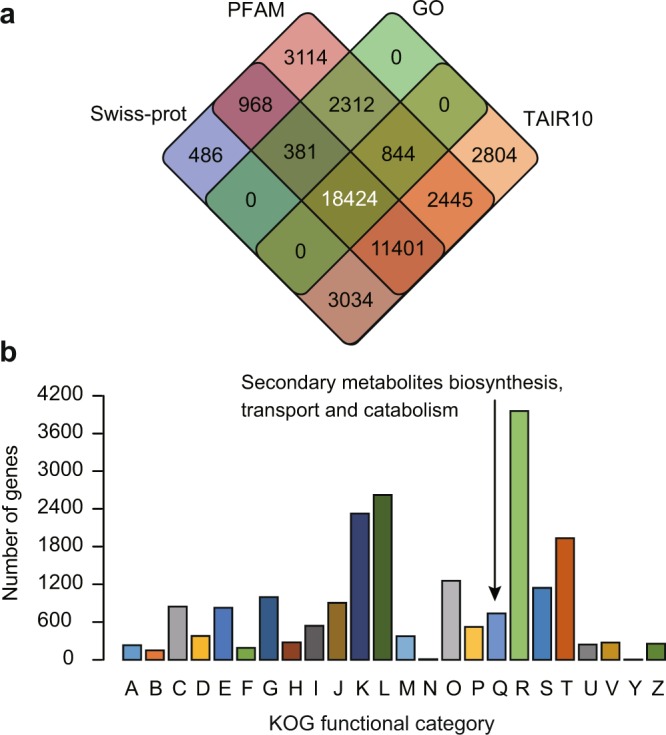
Functional annotation of the tea plant protein-coding genes. (a) Venn diagram shows the shared and unique annotations among Swiss-prot, PFAM, GO and The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR; version10). (b) Functional classification of tea plant genes using KOG database. The functional categories of KOG are abbreviated. A: RNA processing and modification; B: chromatin structure and dynamics; C: energy production and conversion; D: cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; E: amino acid transport and metabolism; F: nucleotide transport and metabolism; G: carbohydrate transport and metabolism; H: coenzyme transport and metabolism; I: lipid transport and metabolism; J: translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K: transcription; L: replication, recombination and repair; M: cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N: cell motility; O: posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; P: inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q: secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; R: general function prediction only; S: function unknown; T: signal transduction mechanisms; U: intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; V: defense mechanisms; Y: nuclear structure; and Z: cytoskeleton.
