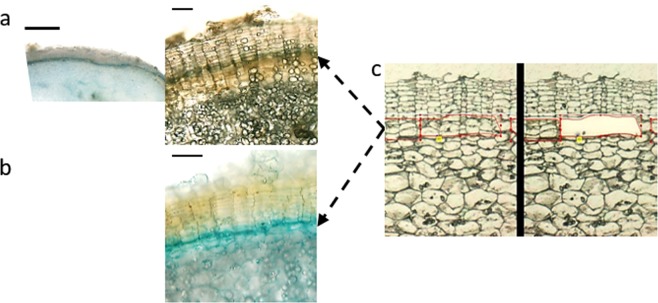
Figure 1.
Visualization of the phellogen layer. A GUS reporter assay (a,b) was used to examine the phellogen layer. Microtubers were induced from transgenic potato plants carrying GUS fused to (a) the promoter region of the MITOTIC CYCLIN B1 gene or (b) the Arabidopsis cytokinin responsive element ARR5, and sections of microtubers were subjected to GUS (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucuronide) staining. Phellogen appears as blue layer (black arrows). Laser capture microdissection was used to isolate the phellogen cells (c, outlined in red) – left panel, before excision of the phellogen; right panel after the excision. Potato skin is characterized by well-organized columns of phellem cells. The phellogen layer is located just below the phellem, each cambial cell at the base of a phellem column. The actively dividing phellogen cells can be easily identified by their puffy morphology (c). Thin bars: 100 µm; thick bar: 1000 µm.