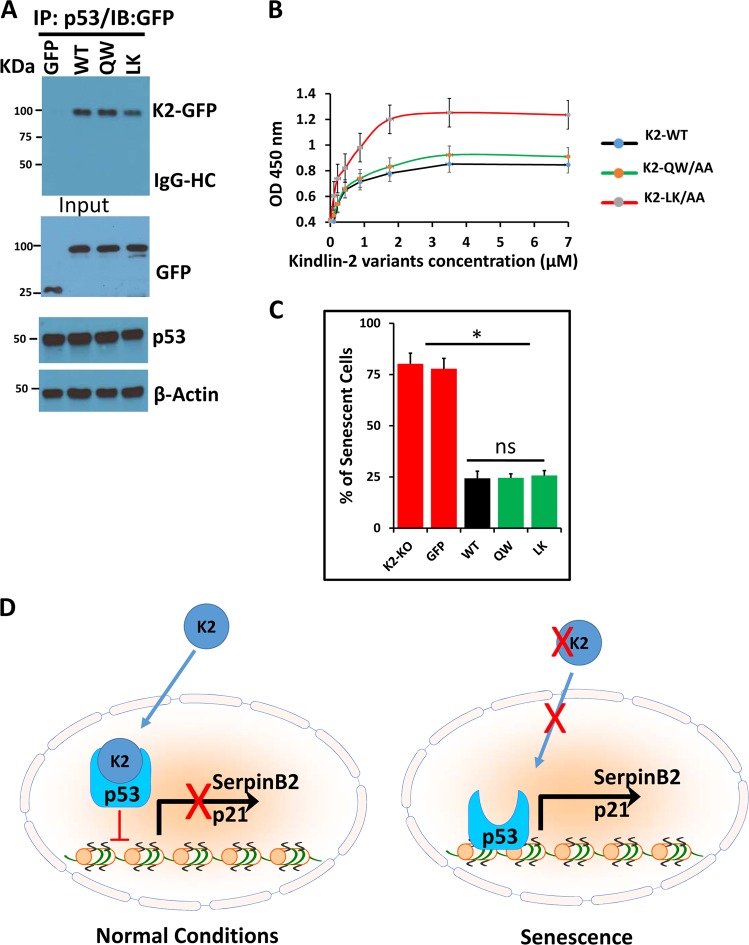
Fig. 6. The Kindlin-2-mediated regulation of senescence may not depend on its binding to integrin or actin.
a Kindlin-2 deficient (K2-KO) MDA-MB-231cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors for control GFP, wild-type Kindlin-2, QW/AA-Kindlin-2 or LK/AA-Kindlin-2 mutants fused to GFP. The corresponding total protein lysates were used for immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-p53 antibody, and subjected to immunoblotting analysis with mouse anti-GFP antibody (upper panel). In control blots (Input blots), the same cell lysates were also immunoblotted with mouse anti-GFP and rabbit anti-p53 antibodies to show the presence of equal amounts of these proteins in the cell lysates. β-Actin is a loading control. b Interaction of Kindlin-2-GST with purified p53. The binding isotherms of increasing concentrations of GST-tagged WT Kindlin-2 and its mutant variants Kindlin-2 (QW/AA) and Kindlin-2 (LK/AA) to the wells of microtiter plates coated with p53. The data are expressed as means ± SEM of triplicates of two representative experiments. c Quantification of SA β-galactosidase staining in the Kindlin-2-deficient (K2-KO) MDA-MB-23 and the K2-KO cells transfected with the control GFP, wild type Keindlin-2 (WT), QW/AA (QW) or LK/AA (LK) Kindlin-2 mutants. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments (*p < 0.05, student t-test). d Model describing the role of Kindlin-2 in the regulation of senescence in breast cancer