Figure 1.
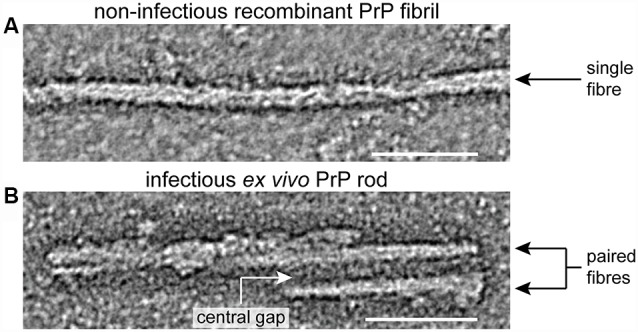
Structural differences between infectious ex vivo PrP rods and non-infectious recombinant prion protein (PrP) fibrils generated in vitro. Panels (A,B) show sections from negative stain electron tomography reconstructions that were originally published in (Terry et al., 2016), scale bars, 50 nm. Non-infectious recombinant PrP fibrils (A) appear as single fibers ~10 nm wide comprised of two closely intertwined protofilaments (Tattum et al., 2006; Terry et al., 2016). In contrast infectious ex vivo PrP rods (B) are ~20 nm wide and are composed of two fibers (each with a double helical substructure) separated by a central gap of 8–10 nm in width which is filled with irregularly structured material (Terry et al., 2016, 2019).
